Top RMM tools are revolutionizing how businesses manage their IT infrastructure. These powerful solutions provide a centralized platform for monitoring, managing, and securing endpoints, networks, and servers, all from a single pane of glass. By automating tasks, proactively identifying and addressing issues, and providing valuable insights into IT performance, RMM tools empower IT teams to work smarter, not harder, and deliver exceptional service to their organizations.
Table of Contents
This article delves into the world of RMM tools, exploring their key features, benefits, and considerations for selecting the right solution. We’ll examine leading RMM providers, discuss best practices for implementation, and highlight real-world success stories. Join us as we uncover how RMM tools are transforming IT management and empowering businesses to achieve their goals.
Introduction to RMM Tools

Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools are software solutions that allow businesses to remotely monitor and manage their IT infrastructure. These tools provide a centralized platform for managing various aspects of a network, including computers, servers, and mobile devices.
RMM tools are essential for businesses of all sizes, particularly those with distributed workforces or complex IT environments. They offer a comprehensive approach to IT management, enabling organizations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance security.
Key Functionalities of RMM Tools
RMM tools offer a wide range of functionalities designed to streamline IT management tasks. Here are some of the key features:
- Remote Monitoring: RMM tools allow IT administrators to monitor the health and performance of devices remotely. This includes tracking system uptime, resource utilization, and network connectivity. By proactively identifying issues, administrators can address them before they escalate into major problems.
- Patch Management: Keeping software up-to-date is crucial for security and stability. RMM tools automate patch management, ensuring that devices receive the latest security updates and bug fixes. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
- Endpoint Management: RMM tools provide a centralized platform for managing endpoints, such as computers, laptops, and mobile devices. This includes tasks like software deployment, configuration management, and asset tracking. By streamlining endpoint management, RMM tools reduce administrative overhead and improve efficiency.
- Remote Control: RMM tools enable IT administrators to remotely access and control devices. This allows them to troubleshoot problems, install software, and perform other tasks without physically being present at the device location. Remote control capabilities are particularly useful for supporting remote workers or managing devices in geographically dispersed locations.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM tools provide detailed reporting and analytics on device performance, security events, and other IT metrics. This data helps IT teams identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions about IT infrastructure management.
Benefits of Using RMM Tools
RMM tools offer numerous benefits to businesses, including:
- Improved IT Efficiency: RMM tools automate many IT tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives. This improves overall IT efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced IT Costs: By automating tasks and streamlining workflows, RMM tools can significantly reduce IT operational costs. They also help minimize downtime and prevent costly outages, further contributing to cost savings.
- Enhanced Security: RMM tools play a vital role in protecting businesses from cyber threats. They provide comprehensive security features, including vulnerability scanning, malware detection, and endpoint protection. By proactively identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, RMM tools help minimize the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Improved User Experience: RMM tools help ensure that users have a positive and productive IT experience. By proactively addressing issues, maintaining system stability, and providing timely support, RMM tools enhance user satisfaction and productivity.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RMM tools are designed to scale with the needs of growing businesses. They offer flexible solutions that can adapt to changing IT environments and support diverse business requirements.
Key Features of Top RMM Tools
RMM tools are designed to streamline and automate various IT tasks, providing a comprehensive solution for managing endpoints and networks. Their key features empower IT professionals to manage devices effectively, enhance security, and optimize performance.
Remote Access
Remote access is a fundamental feature of RMM tools, enabling IT teams to connect to and manage devices remotely. This capability is crucial for troubleshooting issues, installing software, and performing other administrative tasks without physically being present at the device’s location.
Remote access allows IT professionals to provide quick and efficient support, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity.
Patch Management
Patch management is a critical aspect of endpoint security, ensuring that devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and software updates. RMM tools automate this process, scanning for missing patches, downloading updates, and deploying them across the network.
Automated patch management reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security encompasses various measures to protect devices from malware, ransomware, and other threats. RMM tools offer a range of endpoint security features, including:
- Antivirus and anti-malware protection
- Firewall management
- Intrusion detection and prevention
- Data loss prevention
Comprehensive endpoint security features are essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining network integrity.
Reporting
RMM tools provide detailed reports on various aspects of IT operations, including:
- Device inventory
- Software usage
- Security events
- Patching status
Reporting capabilities enable IT teams to gain insights into their IT environment, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Other Notable Features
Beyond the core features, RMM tools often offer additional functionalities such as:
- Asset management: Tracking hardware and software assets across the network
- Script automation: Automating repetitive tasks through custom scripts
- Remote deployment: Deploying software and applications remotely
- User management: Managing user accounts and permissions
- Alerting and notifications: Receiving alerts about critical events and issues
Top RMM Tools in the Market
The RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) market is filled with numerous solutions, each offering a unique set of features and capabilities. Selecting the right RMM tool can be challenging, as it requires considering factors such as pricing, features, target audience, and scalability. This section provides a comprehensive overview of some of the leading RMM tools in the market, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Top RMM Tools in the Market
| Tool Name | Pricing Model | Key Features | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | Subscription-based, with various plans | Remote access, patch management, endpoint monitoring, scripting, ticketing, reporting, integrations | Small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and managed service providers (MSPs) |
| ConnectWise Automate | Subscription-based, with various plans | Comprehensive automation, remote control, patch management, scripting, reporting, integrations | MSPs and large enterprises |
| Datto RMM | Subscription-based, with various plans | Remote access, endpoint monitoring, patch management, scripting, reporting, backup and disaster recovery | MSPs and large enterprises |
| NinjaOne | Subscription-based, with various plans | Remote access, endpoint monitoring, patch management, scripting, reporting, integrations | MSPs and small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) |
Atera is a popular choice for SMBs and MSPs due to its user-friendly interface, affordable pricing, and comprehensive features. It offers a wide range of features, including remote access, patch management, endpoint monitoring, scripting, ticketing, and reporting. However, Atera’s advanced features may be limited for larger enterprises with complex IT environments. ConnectWise Automate is a powerful RMM tool that caters to MSPs and large enterprises. It boasts a comprehensive set of automation features, allowing for streamlined IT operations. ConnectWise Automate’s extensive capabilities come at a higher price point, making it a more suitable option for organizations with larger budgets. Datto RMM focuses on providing a robust solution for MSPs and large enterprises, emphasizing backup and disaster recovery capabilities. Datto’s platform integrates seamlessly with its other products, such as Datto Backup and Datto SIRIS, offering a comprehensive IT management solution. However, Datto RMM can be complex to set up and manage, requiring a higher level of technical expertise. NinjaOne offers a flexible and scalable RMM solution for MSPs and SMBs. Its intuitive interface and comprehensive feature set make it a popular choice for organizations of all sizes. NinjaOne’s pricing model is competitive, making it a cost-effective option for businesses with limited budgets. However, NinjaOne’s advanced features may not be as extensive as those offered by other leading RMM tools.
Top RMM tools help you manage your IT infrastructure efficiently, but sometimes you need a creative outlet. If you’re looking for a powerful and free digital painting program, you can download Krita here. Once you’ve unleashed your artistic side, you can return to managing your systems with those robust RMM tools.
RMM Tool Use Cases
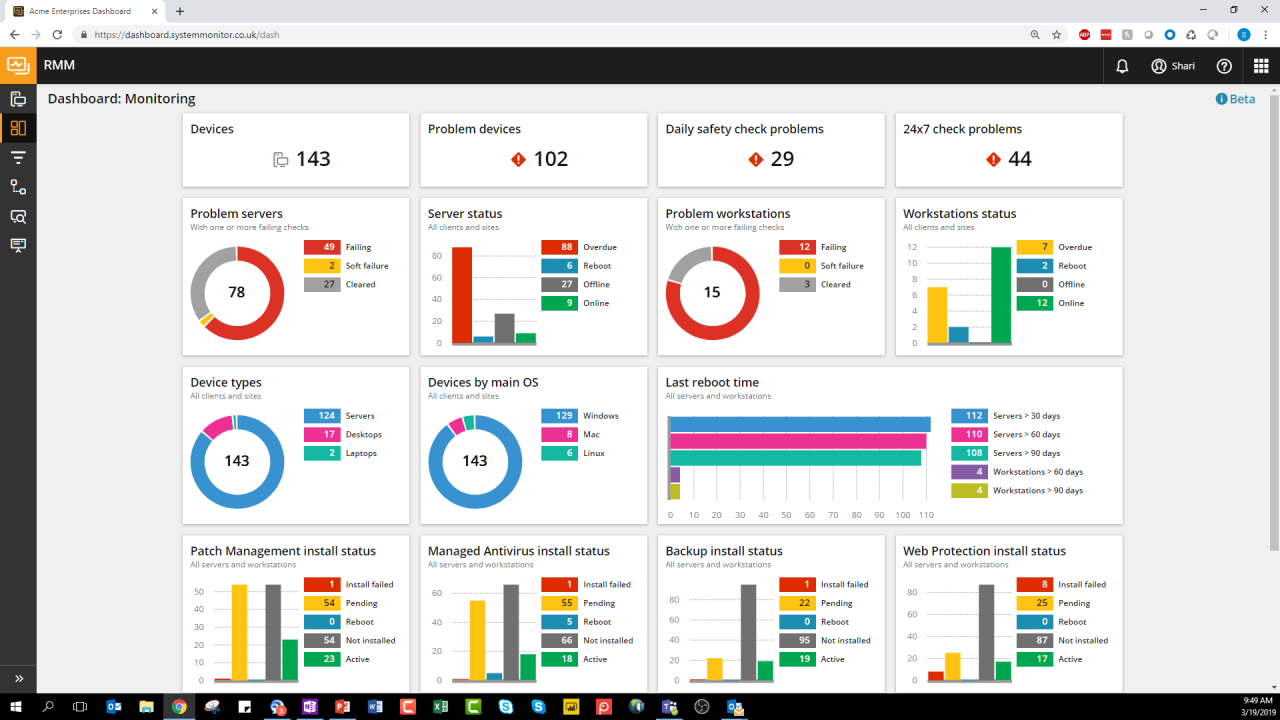
RMM tools offer a comprehensive suite of features that streamline IT operations and enhance efficiency across various IT environments. They empower IT professionals to manage and monitor devices, automate tasks, and proactively address potential issues, ultimately improving overall productivity and security.
IT Support
RMM tools are invaluable for IT support teams, enabling them to provide efficient and effective assistance to end-users. By centralizing device management, monitoring, and remote access capabilities, RMM tools streamline troubleshooting and resolution processes.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM tools allow IT support teams to remotely access and control devices, enabling them to diagnose and resolve issues without requiring physical presence. This reduces downtime and improves response times, ensuring users experience minimal disruption.
- Automated Patching and Updates: RMM tools automate the process of patching and updating software, ensuring that devices are protected from vulnerabilities and running the latest versions. This minimizes the risk of security breaches and system instability.
- Proactive Monitoring and Alerts: RMM tools continuously monitor devices for performance issues, hardware failures, and security threats. They generate alerts when problems are detected, allowing IT support teams to proactively address issues before they escalate and impact end-users.
- Ticket Management and Reporting: RMM tools integrate with ticketing systems, providing a centralized platform for managing support requests, tracking progress, and generating reports on IT support performance.
Security Management
RMM tools play a critical role in enhancing security posture and mitigating risks. They provide comprehensive security management capabilities, including vulnerability scanning, endpoint protection, and data loss prevention.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM tools regularly scan devices for vulnerabilities, identifying potential security weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers. This allows IT teams to prioritize patching and remediation efforts, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Endpoint Protection: RMM tools offer endpoint protection features, such as antivirus, anti-malware, and firewall management, to protect devices from malicious software and unauthorized access. This ensures that sensitive data is protected and systems remain secure.
- Data Loss Prevention: RMM tools can enforce data loss prevention policies, preventing sensitive information from being transmitted or copied to unauthorized devices or locations. This helps to protect confidential data from accidental or malicious leaks.
Network Monitoring
RMM tools provide valuable network monitoring capabilities, enabling IT teams to track network performance, identify bottlenecks, and proactively address potential issues. This ensures optimal network availability and performance, enhancing user experience and productivity.
- Network Performance Monitoring: RMM tools monitor network traffic, bandwidth utilization, and latency, providing insights into network performance and identifying potential bottlenecks. This allows IT teams to optimize network configuration and resource allocation, improving overall network efficiency.
- Network Device Monitoring: RMM tools can monitor the health and performance of network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. They generate alerts when problems are detected, allowing IT teams to proactively address issues and prevent network outages.
- Network Security Monitoring: RMM tools can monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or malware infections. This helps to identify and mitigate security threats before they impact the network or devices.
Asset Management
RMM tools streamline asset management processes, providing a centralized platform for tracking hardware and software assets across the IT environment. This enables IT teams to optimize asset utilization, reduce costs, and improve compliance.
- Hardware and Software Inventory: RMM tools automatically inventory hardware and software assets, providing a comprehensive view of the IT environment. This allows IT teams to track asset lifecycles, optimize resource allocation, and ensure compliance with software licensing agreements.
- Asset Lifecycle Management: RMM tools facilitate asset lifecycle management, from procurement to disposal. They provide tools for tracking asset usage, scheduling maintenance, and managing asset retirement, ensuring efficient asset utilization and cost optimization.
- Software License Compliance: RMM tools help to ensure software license compliance by tracking software installations and usage. This minimizes the risk of software audits and penalties, ensuring that organizations are using software legally and efficiently.
Security Considerations: Top Rmm Tools
RMM tools, while offering significant benefits for managing IT infrastructure, also introduce security risks that must be carefully considered. These tools have access to sensitive data and systems, making it crucial to implement robust security measures to protect both your organization and your clients.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information stored and transmitted by RMM tools. Encryption converts data into an unreadable format, preventing unauthorized access.
- RMM tools should use strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, to ensure data security.
- Data encryption should be applied at rest (when data is stored) and in transit (when data is being transmitted).
- Organizations should ensure that their RMM tools support end-to-end encryption, where data is encrypted from the source to the destination, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access during transmission.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems managed by RMM tools.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to grant different levels of access based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to require users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access to the RMM tool.
- Regularly review user access permissions and revoke access for former employees or contractors.
Security Audits
Regular security audits are crucial for identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities in RMM tools.
- Conduct periodic security audits to assess the effectiveness of security controls and identify any weaknesses.
- Engage independent security professionals to conduct penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Review security logs regularly to detect any suspicious activity or security breaches.
Best Practices for Maintaining Security
- Keep RMM tools and software up-to-date: Regularly update RMM tools and software to patch vulnerabilities and improve security.
- Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication: Securely protect access to the RMM tool with strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
- Limit access to sensitive data: Only grant access to sensitive data on a need-to-know basis.
- Implement a robust security policy: Develop a comprehensive security policy that Artikels security procedures, access controls, and incident response plans.
- Educate users about security best practices: Train users on security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and reporting suspicious activity.
- Monitor security events and respond promptly: Regularly monitor security events and respond promptly to any security incidents.
Future Trends in RMM
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the changing needs of businesses. Emerging trends are shaping the future of RMM tools, leading to more sophisticated and automated solutions.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation
AI and automation are transforming the IT industry, and RMM is no exception. AI-powered features are being integrated into RMM tools to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. For example, AI algorithms can analyze data from multiple sources to predict potential issues before they occur, allowing IT teams to proactively address them. Automation can streamline repetitive tasks, such as software updates and patch management, freeing up IT professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives.
The Future Direction of RMM Tools
RMM tools are evolving to become more comprehensive and integrated. They are moving beyond traditional remote management capabilities to encompass a wider range of IT functions, including:
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response: RMM tools are increasingly incorporating security features, such as real-time threat detection, endpoint security, and vulnerability management. This allows IT teams to proactively monitor for security threats and respond quickly to incidents.
- Cloud Management: As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based services, RMM tools are adapting to manage cloud environments. This includes monitoring cloud infrastructure, managing cloud applications, and ensuring compliance with cloud security standards.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: RMM tools are leveraging data analytics to provide valuable insights into IT operations. This allows IT teams to identify trends, optimize performance, and make data-driven decisions.
The Role of RMM Tools in Modern IT Management
RMM tools are becoming essential for modern IT management, enabling businesses to:
- Improve IT Efficiency: RMM tools automate repetitive tasks, reduce manual intervention, and streamline IT processes, leading to increased efficiency.
- Enhance Security Posture: RMM tools provide real-time security monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and incident response capabilities, strengthening the overall security posture.
- Reduce Costs: By automating tasks and proactively addressing issues, RMM tools help reduce IT costs associated with downtime, maintenance, and support.
- Improve User Experience: RMM tools enable IT teams to provide faster and more efficient support, leading to a better user experience.
Best Practices for Using RMM Tools
RMM tools can significantly improve IT efficiency and security, but their effectiveness depends on how they are implemented and managed. By following best practices, organizations can maximize the benefits of RMM tools and ensure their IT infrastructure is protected and optimized.
Efficient Monitoring
Efficient monitoring is essential for proactive problem identification and resolution. RMM tools provide real-time visibility into system health and performance, enabling IT teams to identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Establish clear monitoring thresholds: Define specific performance metrics and thresholds that trigger alerts when critical values are exceeded. This allows for timely intervention and prevents minor issues from becoming major problems.
- Configure automated alerts: Set up automated alerts for critical events, such as system failures, security breaches, or hardware failures. This ensures prompt notification and facilitates rapid response.
- Leverage real-time dashboards: Utilize the real-time dashboards provided by RMM tools to gain a comprehensive overview of system performance and identify any anomalies or trends.
- Integrate with other monitoring tools: Integrate RMM tools with other monitoring systems, such as network monitoring tools, to gain a holistic view of the IT environment and streamline troubleshooting.
Proactive Maintenance
Proactive maintenance is crucial for preventing system failures and downtime. RMM tools can automate routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates, patch management, and system optimization, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and ensuring optimal performance.
- Schedule automated tasks: Utilize the scheduling capabilities of RMM tools to automate routine maintenance tasks, such as software updates, antivirus scans, and disk cleanup. This ensures tasks are performed consistently and efficiently, without requiring manual intervention.
- Implement patch management policies: Create and enforce patch management policies to ensure all systems are updated with the latest security patches and bug fixes. This reduces the risk of vulnerabilities and protects against known exploits.
- Optimize system performance: Utilize RMM tools to monitor system performance and identify potential bottlenecks. This allows for proactive optimization, ensuring smooth operation and maximizing system efficiency.
- Conduct regular health checks: Schedule regular system health checks using RMM tools to identify potential issues before they escalate. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures system stability.
Incident Response
Effective incident response is critical for minimizing the impact of security breaches and system failures. RMM tools provide the necessary tools and insights to quickly identify, contain, and resolve incidents.
- Establish clear incident response protocols: Define clear procedures for responding to security incidents, including escalation paths, communication protocols, and remediation steps. This ensures a coordinated and efficient response.
- Leverage remote access capabilities: Utilize the remote access capabilities of RMM tools to troubleshoot and resolve issues remotely, minimizing downtime and inconvenience. This is especially valuable for addressing security incidents or critical system failures.
- Utilize automated incident reporting: Configure RMM tools to generate automated reports on security incidents, system failures, or other critical events. This provides a detailed record of incidents and facilitates root cause analysis.
- Integrate with security information and event management (SIEM) tools: Integrate RMM tools with SIEM systems to centralize security data and gain a comprehensive view of security threats and incidents.
Regular Reviews and Optimization
Regular reviews and optimization of RMM tool configurations are essential for ensuring their effectiveness and maximizing their benefits. This includes evaluating current settings, identifying areas for improvement, and making necessary adjustments.
- Review monitoring thresholds and alerts: Regularly review the monitoring thresholds and alerts configured in the RMM tool to ensure they are still relevant and effective. Adjust thresholds as needed to reflect changes in system performance or security requirements.
- Optimize automated tasks: Evaluate the automated tasks scheduled in the RMM tool and make adjustments to improve efficiency or address new requirements. This ensures that tasks are performed optimally and meet current needs.
- Evaluate incident response protocols: Regularly review and update incident response protocols to ensure they are aligned with current security threats and best practices. This ensures a timely and effective response to incidents.
- Stay updated with the latest RMM features: RMM tools are constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being added regularly. Stay informed about the latest updates and consider adopting new features that can enhance security and efficiency.
Real-World Examples of RMM Tool Success Stories
RMM tools have proven their value in various industries, helping businesses of all sizes streamline their IT operations, enhance security, and improve overall efficiency. Examining real-world success stories provides valuable insights into the tangible benefits and impactful outcomes achieved by organizations that have embraced RMM solutions.
Success Stories from Different Industries
The benefits of RMM tools extend across diverse industries. Here are examples of businesses that have successfully implemented RMM tools and reaped significant rewards:
- Healthcare: A large hospital network deployed an RMM solution to manage its vast IT infrastructure, encompassing hundreds of workstations, servers, and medical devices. The RMM tool enabled the IT team to automate routine tasks like software updates and patch management, freeing up valuable time for more strategic initiatives. The hospital network also experienced a significant reduction in security vulnerabilities and incidents, as the RMM tool proactively monitored and patched systems, mitigating potential threats.
- Education: A university with a large student body implemented an RMM solution to manage its computer labs and student devices. The RMM tool enabled the IT team to remotely access and troubleshoot student devices, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing downtime during critical periods like exams. The university also benefited from centralized software deployment and patch management, streamlining IT operations and improving efficiency.
- Financial Services: A financial services firm implemented an RMM solution to enhance its cybersecurity posture and comply with industry regulations. The RMM tool provided real-time monitoring of critical systems and alerted the IT team to any suspicious activity, allowing for immediate intervention and mitigation of potential threats. The firm also benefited from automated vulnerability scanning and patch management, ensuring its systems remained secure and compliant.
- Manufacturing: A manufacturing company deployed an RMM solution to manage its production line systems and ensure operational continuity. The RMM tool enabled the IT team to remotely monitor and manage critical systems, ensuring minimal downtime and maximizing productivity. The company also benefited from proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, minimizing disruptions and ensuring smooth production operations.
Key Factors Contributing to Success
The success of RMM tool implementation often hinges on several key factors:
- Proper Planning and Implementation: Thorough planning is crucial to ensure the RMM solution aligns with the organization’s specific needs and goals. This involves identifying the key functionalities required, selecting the right tool, and developing a comprehensive implementation strategy.
- Strong IT Team Support: A dedicated and skilled IT team is essential to effectively utilize and manage the RMM solution. The team should be well-trained on the tool’s features and functionalities, ensuring optimal performance and problem resolution.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Ongoing monitoring of the RMM solution’s performance and effectiveness is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and maximizing its value. Regularly reviewing and adjusting settings, as well as proactively addressing any issues, ensures the tool remains relevant and effective.
- Employee Training and Awareness: End-user training and awareness are essential for maximizing the benefits of an RMM solution. By educating employees about the tool’s capabilities and how to use it effectively, organizations can foster a more secure and efficient IT environment.
Analyzing the Benefits Achieved, Top rmm tools
The successful implementation of RMM tools has consistently yielded significant benefits for organizations across various industries.
- Improved Efficiency: By automating routine tasks such as software updates, patch management, and remote access, RMM tools free up IT teams to focus on more strategic initiatives. This improved efficiency translates into reduced operational costs and enhanced productivity.
- Reduced Costs: RMM tools can help organizations save money in various ways. By automating tasks, reducing downtime, and minimizing security incidents, these solutions can significantly reduce operational expenses and IT-related costs.
- Enhanced Security: RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of systems, automated vulnerability scanning, and proactive patch management, significantly reducing the risk of security breaches and data loss. This enhanced security posture is crucial for organizations in all industries, especially those handling sensitive data.
- Improved Compliance: RMM tools can help organizations comply with industry regulations and security standards. By automating tasks like vulnerability scanning and patch management, these solutions ensure that systems remain compliant and meet the necessary requirements.
Conclusion
This comprehensive exploration of RMM tools has highlighted their critical role in modern IT management. From streamlining routine tasks to proactively addressing security threats, RMM solutions empower IT professionals to optimize performance, enhance security, and deliver exceptional user experiences.
Key Takeaways
This article has shed light on several key aspects of RMM tools:
- Comprehensive Overview: We’ve explored the core functionalities of RMM tools, covering patch management, remote access, software deployment, and more.
- Top RMM Tools: We’ve reviewed leading RMM solutions in the market, highlighting their strengths and unique features.
- Real-World Use Cases: We’ve delved into practical scenarios where RMM tools have proven invaluable, demonstrating their effectiveness in various IT environments.
- Security Considerations: We’ve emphasized the importance of robust security measures within RMM tools, emphasizing data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls.
- Future Trends: We’ve examined emerging trends in RMM, such as the integration of AI and automation, to anticipate future advancements in the field.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, RMM tools are indispensable for modern IT management. By streamlining tasks, enhancing security, and providing valuable insights, RMM solutions empower IT teams to work efficiently, proactively address issues, and ensure the smooth operation of business-critical systems. As you embark on your journey to choose and implement an RMM tool, remember to consider your specific needs, budget, and future growth plans. The right RMM solution can significantly improve your IT infrastructure’s performance, security, and overall efficiency.
