RMM tools for MSPs have revolutionized the way managed service providers manage their clients’ IT infrastructure. These powerful tools offer a comprehensive suite of features, including remote monitoring, device management, patch management, and security, enabling MSPs to provide proactive and efficient IT support.
Table of Contents
By leveraging automation, RMM tools free up MSPs from tedious manual tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives and deliver exceptional client experiences. This has led to a significant shift in the MSP landscape, with RMM tools becoming an indispensable part of their operations.
Choosing the Right RMM Tool for Your MSP

Selecting the right RMM tool is crucial for any MSP looking to streamline operations, enhance security, and improve client satisfaction. An RMM tool can automate tasks, monitor systems, and provide valuable insights into your clients’ IT infrastructure, ultimately freeing up your team to focus on higher-value activities. But with so many options available, choosing the best fit for your specific needs can be a challenge.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an RMM Tool
It’s essential to carefully evaluate your MSP’s unique requirements before embarking on the RMM tool selection process. This includes considering your budget, the size of your client base, and your team’s technical expertise.
- Budget: RMM tools come with varying pricing models, ranging from monthly subscriptions to per-device fees. Determine your budget constraints and look for a tool that offers a cost-effective solution without compromising on essential features.
- Client Base Size: The size of your client base will influence your RMM tool requirements. For small MSPs with a limited number of clients, a basic RMM tool might suffice. However, larger MSPs with a diverse client base may need a more comprehensive solution with advanced features and scalability.
- Technical Expertise: Consider your team’s technical expertise and the level of support required. Some RMM tools are more user-friendly and require minimal technical knowledge, while others offer advanced features that demand specialized skills. Choose a tool that aligns with your team’s capabilities and training resources.
Comparing Popular RMM Tools
Several popular RMM tools cater to MSPs, each offering a unique set of features, pricing models, and customer reviews. Here’s a comparison of some notable options:
| RMM Tool | Features | Pricing | Customer Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | Remote access, patch management, endpoint monitoring, ticketing system, reporting | Starts at $79 per technician per month | Generally positive reviews, praised for its user-friendliness and comprehensive features |
| ConnectWise Automate | Extensive automation capabilities, scripting, advanced reporting, integrations with other IT tools | Pricing varies based on the number of endpoints and features | Highly regarded for its robust features and scalability, but some users find it complex |
| Datto RMM | Cloud-based platform, remote access, endpoint monitoring, vulnerability scanning, backup and disaster recovery | Pricing based on the number of endpoints and features | Known for its reliable backup and disaster recovery capabilities, but some users find it expensive |
| NinjaOne | Remote access, endpoint monitoring, patch management, scripting, ticketing system, reporting | Starts at $39 per technician per month | Positive reviews for its ease of use, intuitive interface, and competitive pricing |
Decision-Making Framework for Choosing an RMM Tool
To make an informed decision, consider the following framework:
1. Define your requirements: Clearly identify your MSP’s specific needs, including budget, client base size, and technical expertise.
2. Research and compare options: Explore different RMM tools and evaluate their features, pricing, and customer reviews.
3. Request demos and trials: Schedule demos with shortlisted RMM vendors to get hands-on experience with the platform.
4. Consider integrations: Ensure the RMM tool integrates seamlessly with your existing IT tools and workflows.
5. Evaluate customer support: Assess the vendor’s customer support quality and responsiveness.
6. Make a decision: Based on your evaluation, choose the RMM tool that best aligns with your requirements and budget.
RMM Tools and Automation
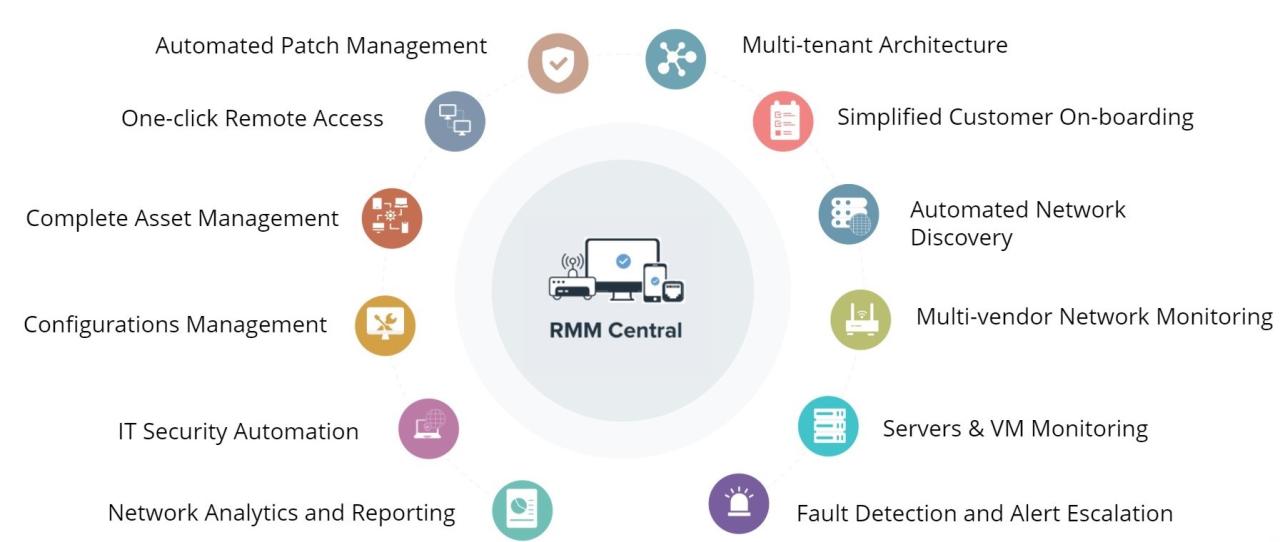
RMM tools are designed to automate various tasks and processes, significantly reducing manual labor for MSPs. Automation is a core feature of RMM solutions, empowering MSPs to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and deliver better services.
Automation Capabilities
RMM tools offer a wide range of automation capabilities, enabling MSPs to streamline their workflows and optimize resource utilization. Here are some key areas where RMM tools excel in automation:
- Automated Tasks: RMM tools can automate repetitive tasks such as software updates, patch management, and system backups. This frees up technicians to focus on more complex issues and proactive maintenance.
- Workflow Automation: RMM tools allow you to create custom workflows that automate complex tasks involving multiple steps. For example, you can create a workflow that automatically triggers a system scan, identifies vulnerabilities, and applies patches if needed.
- Reporting Automation: RMM tools can generate automated reports on various aspects of IT infrastructure, such as system health, security vulnerabilities, and software licenses. This provides valuable insights for proactive maintenance and informed decision-making.
Benefits of Automation
Automation brings significant benefits to MSPs, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing service quality. Here are some key advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation eliminates manual tasks, allowing technicians to focus on higher-value activities like troubleshooting complex issues and providing proactive support.
- Reduced Costs: By automating tasks, MSPs can reduce labor costs and improve resource utilization. This translates to lower operational expenses and higher profitability.
- Improved Service Quality: Automation ensures consistent and reliable service delivery. Automated tasks are performed with precision and accuracy, minimizing errors and improving the overall quality of service.
- Enhanced Security: Automation helps improve security by automating tasks like patch management and vulnerability scanning, reducing the risk of security breaches.
Real-World Examples, Rmm tools for msp
Here are some real-world scenarios where RMM tools can be used to automate tasks:
- Software Updates: An RMM tool can be configured to automatically scan for and install software updates on all managed devices. This ensures that systems are always running the latest versions, reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities and improving performance.
- Backup Automation: RMM tools can automate daily backups of critical data, ensuring that data is protected in case of hardware failures or other disasters. This reduces the risk of data loss and improves business continuity.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM tools can automate vulnerability scanning, identifying potential security weaknesses in managed systems. This allows MSPs to proactively address vulnerabilities before they are exploited by attackers.
- Incident Response: RMM tools can be configured to automatically trigger alerts and escalate incidents based on predefined criteria. This allows MSPs to respond to security threats or system failures quickly and efficiently.
The Future of RMM Tools: Rmm Tools For Msp
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the growing demand for sophisticated IT solutions. The future holds exciting possibilities for RMM tools, with emerging trends poised to reshape the way MSPs manage their clients’ IT infrastructure.
AI-Powered Monitoring and Predictive Analytics
AI is revolutionizing the way RMM tools operate. AI-powered monitoring can proactively identify potential issues before they become critical, significantly reducing downtime and improving overall system performance. This is achieved by analyzing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and predicting potential problems.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI can analyze historical data on hardware and software performance to predict when components are likely to fail. This allows MSPs to schedule maintenance proactively, preventing costly downtime and ensuring optimal system performance.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can automate incident response by identifying and resolving common issues without human intervention. This frees up MSP technicians to focus on more complex tasks and improves the overall efficiency of IT operations.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI can provide personalized recommendations based on individual client needs and system configurations. This helps MSPs tailor their services to specific client requirements, ensuring optimal performance and security.
The Impact of 5G and Edge Computing
The rise of 5G and edge computing is transforming the way RMM tools interact with devices and data. 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency enable faster data transfer and real-time monitoring of remote devices, while edge computing brings processing power closer to the data source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness.
- Remote Device Management: 5G and edge computing enable more efficient management of remote devices, including IoT devices, with real-time monitoring and control capabilities. This allows MSPs to provide seamless support for distributed networks, even in remote locations.
- Enhanced Security: Edge computing allows for localized security measures, reducing the risk of data breaches and improving overall security posture. RMM tools can leverage edge computing to implement more robust security protocols and protect sensitive data.
- Improved Performance: By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and improves application performance. This is particularly beneficial for real-time applications, such as video conferencing and online gaming, where responsiveness is critical.
The Future of RMM Tools and Their Impact on MSPs
The future of RMM tools is bright, with advancements in AI, 5G, and edge computing poised to revolutionize the way MSPs manage their clients’ IT infrastructure. RMM tools are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering a wider range of features and capabilities to streamline IT operations and enhance security.
- Proactive and Predictive Management: RMM tools will move beyond reactive troubleshooting to proactive and predictive management, leveraging AI and machine learning to anticipate and prevent issues before they occur.
- Increased Automation: Automation will play a crucial role in the future of RMM tools, automating routine tasks and freeing up MSP technicians to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced Security: RMM tools will continue to evolve to address the growing threat landscape, incorporating advanced security features such as endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat intelligence, and vulnerability management.
Summary
In conclusion, RMM tools are a game-changer for MSPs, empowering them to streamline their operations, enhance security, and deliver exceptional client service. As the IT landscape continues to evolve, RMM tools will play an even more crucial role in helping MSPs navigate the complexities of managing modern IT environments.
RMM tools are essential for MSPs to manage their clients’ IT infrastructure efficiently. These tools can automate tasks, monitor systems, and provide remote access, which saves time and improves service delivery. For example, if you need to research a specific technical topic, you can use a tool like the google books downloader to quickly access relevant information from a wide range of books.
This information can then be used to better understand the problem and provide effective solutions to your clients.
