RMM platform, short for Remote Monitoring and Management platform, is a powerful tool for IT professionals seeking to optimize their workflows and enhance the security of their systems. These platforms empower users to remotely monitor, manage, and secure devices, networks, and applications from a central location, eliminating the need for physical intervention.
Table of Contents
Imagine having a single dashboard that provides real-time insights into the health and performance of your entire IT infrastructure. This is the promise of RMM platforms, offering a comprehensive and unified approach to IT management. With features like automated patching, vulnerability scanning, and remote access, RMM platforms streamline tasks, reduce downtime, and improve overall IT efficiency.
What is an RMM Platform?
An RMM platform, short for Remote Monitoring and Management platform, is a powerful tool for IT professionals to manage and monitor their clients’ computer systems remotely. These platforms offer a centralized dashboard for managing multiple devices, ensuring seamless operations and proactive maintenance.
Core Functionalities of an RMM Platform
RMM platforms offer a wide range of functionalities, including:
- Remote Access and Control: This feature allows technicians to access and control client computers remotely, enabling troubleshooting and software installation without physically being on-site.
- System Monitoring: RMM platforms continuously monitor client systems for performance issues, hardware failures, and security threats. They provide real-time alerts and reports to help IT professionals identify and resolve problems before they escalate.
- Patch Management: RMM platforms automate the process of updating operating systems, software applications, and security patches, ensuring that client systems are protected from vulnerabilities.
- Endpoint Security: Many RMM platforms include built-in security features like antivirus, anti-malware, and firewall management, providing comprehensive protection against cyber threats.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: RMM platforms offer automated backup solutions for client data, ensuring data protection and quick recovery in case of system failures or data loss.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM platforms generate comprehensive reports on system performance, security status, and other key metrics, providing valuable insights for IT professionals to make informed decisions.
Real-world Examples of RMM Platforms and their Applications
There are several popular RMM platforms available in the market, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some popular examples include:
- Datto RMM: This platform is widely used by MSPs (Managed Service Providers) to manage and monitor their clients’ IT infrastructure, offering comprehensive features like remote access, system monitoring, patch management, and security solutions.
- ConnectWise Automate: Another popular RMM platform known for its robust automation capabilities, ConnectWise Automate enables IT professionals to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up time for more strategic initiatives.
- NinjaRMM: This platform focuses on providing a user-friendly interface and intuitive dashboards for managing client systems. NinjaRMM is particularly popular for its ease of use and comprehensive reporting capabilities.
Benefits of Using an RMM Platform
An RMM platform can be a valuable tool for businesses of all sizes, offering a range of advantages that can significantly improve IT efficiency and security. These benefits can translate into cost savings, increased productivity, and a stronger overall IT posture.
Enhanced IT Efficiency
Implementing an RMM solution can significantly streamline IT operations and free up valuable time for your IT team.
- Automated Tasks: RMM platforms automate routine tasks such as software updates, patch management, and system backups. This frees up your IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives and complex problem-solving.
- Remote Management: RMM platforms enable remote access and management of devices, allowing IT professionals to resolve issues quickly and efficiently, regardless of their physical location. This reduces the need for on-site visits, saving time and money.
- Centralized Monitoring: RMM platforms provide a centralized dashboard for monitoring system performance, security alerts, and user activity. This consolidated view gives IT teams a comprehensive understanding of the IT environment, enabling proactive problem-solving and resource allocation.
- Improved Reporting: RMM platforms generate detailed reports on system performance, security vulnerabilities, and user activity. These reports provide valuable insights into IT trends, allowing for data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
Enhanced Security
RMM platforms play a crucial role in bolstering IT security, providing a multi-layered approach to protecting sensitive data and systems.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM platforms regularly scan for security vulnerabilities and provide alerts for potential threats. This proactive approach helps identify and mitigate risks before they can be exploited.
- Endpoint Security: RMM platforms offer comprehensive endpoint security features, including anti-malware protection, firewall management, and data encryption. This helps safeguard devices and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Password Management: RMM platforms can manage and enforce password policies, ensuring strong and secure passwords across the organization. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Compliance Reporting: RMM platforms provide detailed reports on security policies and compliance status, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements and demonstrate due diligence.
Improved Customer Experience
By automating tasks, streamlining IT operations, and ensuring system stability, RMM platforms contribute to a smoother and more efficient user experience.
- Faster Resolution Times: RMM platforms enable IT teams to resolve issues more quickly, minimizing downtime and improving user productivity.
- Proactive Maintenance: RMM platforms facilitate proactive maintenance and troubleshooting, reducing the likelihood of unexpected system failures and disruptions.
- Improved Communication: RMM platforms can facilitate communication between IT staff and users, providing timely updates on system status and maintenance schedules.
Case Studies and Success Stories
- Small Business Example: A small accounting firm implemented an RMM solution to manage their growing IT infrastructure. The platform automated software updates, patch management, and system backups, freeing up their IT staff to focus on client support and other critical tasks. The firm also experienced a significant reduction in downtime and improved overall system stability.
- Large Enterprise Example: A large multinational corporation used an RMM platform to manage its vast IT infrastructure across multiple locations. The platform enabled centralized monitoring, remote management, and automated tasks, resulting in improved efficiency and cost savings. The company also benefited from enhanced security and compliance reporting, which helped them meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive data.
Key Features of RMM Platforms
RMM platforms offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline IT management tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance security. By centralizing monitoring, management, and automation, RMM platforms empower IT professionals to proactively address issues, reduce downtime, and ensure optimal performance.
Remote Monitoring and Management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) are the core functionalities of these platforms. They allow IT professionals to monitor and manage endpoints remotely, regardless of their physical location. This includes:
- Real-time monitoring: RMM platforms provide real-time visibility into the health and performance of endpoints, including system resources, software updates, and security status.
- Remote control: IT professionals can remotely access and control endpoints to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other administrative tasks.
- Automated tasks: RMM platforms automate repetitive tasks, such as software patching, antivirus updates, and system backups, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Patch Management
Patch management is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, ensuring that endpoints are protected against vulnerabilities. RMM platforms offer robust patch management features, including:
- Vulnerability scanning: RMM platforms automatically scan endpoints for vulnerabilities and identify missing patches.
- Patch deployment: They allow IT professionals to deploy patches to endpoints automatically or manually, based on predefined schedules or policies.
- Patch reporting: RMM platforms provide detailed reports on patch status, enabling IT teams to track compliance and identify any issues.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are paramount for any organization. RMM platforms provide various security features, including:
- Antivirus and endpoint protection: RMM platforms integrate with antivirus software and endpoint protection solutions to provide comprehensive security against malware and other threats.
- Firewall management: They allow IT professionals to configure and manage firewalls on endpoints, controlling network traffic and preventing unauthorized access.
- Data loss prevention: RMM platforms can implement data loss prevention (DLP) policies to prevent sensitive information from leaving the network.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM platforms provide detailed reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing IT teams to gain insights into the health and performance of their IT infrastructure. These reports include:
- System performance metrics: RMM platforms track key performance indicators (KPIs), such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and disk space.
- Security alerts and incidents: They generate alerts and reports on security events, such as malware detection, unauthorized access attempts, and system vulnerabilities.
- Compliance audits: RMM platforms can generate reports to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and best practices.
Ticketing and Help Desk
RMM platforms often include ticketing and help desk functionalities, streamlining IT support and communication. These features include:
- Ticket creation and management: IT professionals can create, assign, and track support tickets, ensuring efficient issue resolution.
- Knowledge base integration: RMM platforms can integrate with knowledge bases, providing users with self-service options and reducing the workload on IT support staff.
- Remote assistance: They allow IT professionals to provide remote assistance to users, resolving issues quickly and efficiently.
Integration and Automation
RMM platforms offer integration with other IT tools and services, allowing for greater automation and efficiency. This includes:
- Cloud integration: RMM platforms can integrate with cloud services, such as cloud storage, email, and collaboration tools, extending their functionality and simplifying management.
- API integrations: They provide application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow for integration with third-party applications, extending the platform’s capabilities.
- Workflow automation: RMM platforms enable IT professionals to automate complex tasks, such as provisioning new endpoints, deploying software updates, and responding to security incidents.
Comparison of RMM Features
The following table compares and contrasts different RMM features:
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring and Management | Real-time visibility into endpoint health and performance, remote control, automated tasks | Enables proactive issue resolution, reduces downtime, and improves efficiency |
| Patch Management | Vulnerability scanning, patch deployment, patch reporting | Ensures endpoints are protected against vulnerabilities, improves security posture, and reduces risk |
| Security and Compliance | Antivirus and endpoint protection, firewall management, data loss prevention | Protects endpoints from malware and other threats, enforces security policies, and ensures compliance with regulations |
| Reporting and Analytics | System performance metrics, security alerts and incidents, compliance audits | Provides insights into IT infrastructure health and performance, identifies security threats, and demonstrates compliance |
| Ticketing and Help Desk | Ticket creation and management, knowledge base integration, remote assistance | Streamlines IT support, improves communication, and enhances user experience |
| Integration and Automation | Cloud integration, API integrations, workflow automation | Extends platform functionality, simplifies management, and improves efficiency |
Types of RMM Platforms

RMM platforms are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different types of RMM platforms cater to specific needs and target audiences. Understanding the various types available helps you choose the best platform for your business.
Categorization of RMM Platforms
RMM platforms can be categorized based on their focus and target audience. Here’s a breakdown of common categories:
- MSP-focused RMM Platforms: Designed specifically for Managed Service Providers (MSPs) who manage IT infrastructure for multiple clients. They offer features tailored for managing multiple clients, including remote monitoring and management, patch management, automated tasks, reporting, and billing.
- Small Business RMM Platforms: Target small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with limited IT resources. They offer simplified interfaces and more affordable pricing compared to MSP-focused platforms. These platforms are generally easier to use and manage.
- Enterprise RMM Platforms: Cater to large enterprises with complex IT infrastructure and stringent security requirements. They offer advanced features like comprehensive security monitoring, compliance reporting, and integration with existing enterprise systems.
- Open-Source RMM Platforms: These platforms are free to use and modify, providing greater flexibility and customization. However, they often require more technical expertise to set up and maintain.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Different RMM Platform Types
Each type of RMM platform comes with its own set of strengths and weaknesses.
- MSP-focused RMM Platforms:
- Strengths: Multi-client management, advanced reporting, billing integration, scalability, and automation features.
- Weaknesses: Can be more complex to use, higher pricing, and might not be suitable for smaller businesses with limited IT needs.
- Small Business RMM Platforms:
- Strengths: User-friendly interface, affordable pricing, suitable for managing smaller IT infrastructure, and easy to deploy.
- Weaknesses: Limited features compared to MSP-focused platforms, may not scale well for larger businesses, and might lack advanced security features.
- Enterprise RMM Platforms:
- Strengths: Comprehensive security features, compliance reporting, integration with existing enterprise systems, scalability, and robust automation capabilities.
- Weaknesses: High cost, complex to implement and manage, and might require specialized IT expertise.
- Open-Source RMM Platforms:
- Strengths: Free to use and modify, high flexibility, and customization options.
- Weaknesses: Requires technical expertise to set up and maintain, limited support options, and may not be as feature-rich as commercial platforms.
Examples of RMM Platforms
Here are some examples of RMM platforms within each category:
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| MSP-focused RMM Platforms |
|
| Small Business RMM Platforms |
|
| Enterprise RMM Platforms |
|
| Open-Source RMM Platforms |
|
Choosing the Right RMM Platform
Selecting the right RMM platform is crucial for businesses of all sizes, as it can significantly impact their IT infrastructure management, security posture, and overall operational efficiency. With a plethora of RMM solutions available, choosing the best fit requires careful consideration of various factors.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an RMM Platform
When selecting an RMM platform, it’s essential to consider factors that align with your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. These factors will help you evaluate different solutions and make an informed decision.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Consider your current and future IT infrastructure needs. Choose a platform that can scale with your growth and adapt to changing requirements.
- Features and Functionality: Evaluate the platform’s core features, such as remote access, patch management, endpoint security, and reporting. Ensure it meets your specific needs and provides the necessary tools for effective IT management.
- Ease of Use and User Interface: Opt for a platform with a user-friendly interface that is intuitive for both IT professionals and non-technical users. This will ensure efficient adoption and utilization of the platform.
- Integration Capabilities: Assess the platform’s ability to integrate with existing IT systems and tools, such as ticketing systems, monitoring solutions, and security software. Seamless integration will streamline workflows and improve overall efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: Prioritize security and compliance features. Look for platforms that meet industry standards and offer robust security measures to protect sensitive data and systems.
- Pricing and Support: Compare pricing models and ensure the platform offers affordable pricing that aligns with your budget. Evaluate the level of support provided, including response times, availability, and knowledge base resources.
- Vendor Reputation and Experience: Research the vendor’s reputation, experience, and track record in the industry. Consider factors such as customer reviews, industry recognition, and commitment to innovation.
Decision-Making Framework
To facilitate the evaluation process, consider using a decision-making framework that helps you compare different RMM solutions based on key criteria.
- Define Your Requirements: Begin by clearly outlining your specific IT management needs, including the types of devices to be managed, desired features, and security considerations.
- Shortlist Potential Solutions: Research and identify a shortlist of RMM platforms that meet your initial requirements. Consider vendor reputation, pricing, and feature sets.
- Conduct a Comparative Analysis: Create a table or spreadsheet to compare the shortlisted solutions based on your defined criteria. Evaluate features, pricing, support, and integration capabilities.
- Request Demonstrations: Contact shortlisted vendors and request demonstrations of their platforms. This will allow you to experience the user interface, functionality, and overall usability firsthand.
- Pilot Testing: If possible, consider conducting pilot testing with a limited number of devices to evaluate the platform’s performance and effectiveness in a real-world environment.
- Gather Feedback: Involve your IT team and other relevant stakeholders in the evaluation process. Gather their feedback and perspectives on the shortlisted solutions.
- Make a Decision: Based on your analysis, feedback, and overall assessment, choose the RMM platform that best aligns with your needs, budget, and technical capabilities.
Best Practices for Choosing an RMM Platform
To ensure you choose the right RMM platform, follow these best practices:
- Clearly Define Your Needs: Begin by identifying your specific IT management needs, including the scope of devices to be managed, desired features, and security considerations.
- Research Thoroughly: Conduct in-depth research on various RMM platforms, considering vendor reputation, pricing, features, and customer reviews.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with IT professionals or cybersecurity experts for recommendations and insights on choosing the best RMM solution for your specific needs.
- Consider Future Growth: Select a platform that can scale with your business and adapt to future IT infrastructure changes.
- Prioritize Security and Compliance: Ensure the platform meets industry standards and offers robust security measures to protect sensitive data and systems.
- Evaluate Support and Training: Consider the vendor’s support options, response times, and availability of training resources. This will ensure you receive the necessary assistance to effectively use the platform.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Negotiate: Explore different pricing models and negotiate with vendors to secure the best possible terms and conditions.
Implementation and Integration of RMM Platforms
Implementing an RMM platform involves a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration with your existing IT infrastructure and tools. The process involves careful planning, configuration, and ongoing maintenance to maximize the benefits of the platform.
Steps Involved in Implementing an RMM Platform
Implementing an RMM platform requires a systematic approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize its benefits. Here are the key steps involved:
- Needs Assessment and Goal Definition: Start by clearly defining your organization’s IT management needs and goals. Identify the specific pain points you aim to address with the RMM platform, such as improving security posture, automating tasks, or enhancing IT support efficiency.
- Platform Selection: Research and select an RMM platform that aligns with your needs and budget. Consider factors like features, scalability, pricing, and integration capabilities. Conduct thorough vendor evaluation and request demos to assess the platform’s functionality and usability.
- Deployment and Configuration: Once you’ve chosen a platform, follow the vendor’s instructions for deployment and configuration. This may involve installing agents on managed devices, configuring security settings, and setting up user roles and permissions.
- Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure: Integrate the RMM platform with your existing IT tools, such as Active Directory, ticketing systems, and monitoring tools. This allows for data sharing, automation, and centralized management.
- User Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to your IT team on using the RMM platform. Ensure they understand its features, functionalities, and best practices. This will enable them to effectively manage and leverage the platform.
- Pilot Implementation and Testing: Conduct a pilot implementation on a small group of devices or users to test the platform’s functionality and identify any potential issues. This allows for fine-tuning and optimization before full-scale rollout.
- Full-Scale Rollout and Ongoing Monitoring: Once the pilot implementation is successful, gradually roll out the RMM platform to the entire organization. Regularly monitor the platform’s performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure ongoing security updates.
Integration with Existing IT Infrastructure and Tools
Integrating an RMM platform with existing IT infrastructure and tools is crucial for streamlining operations and maximizing efficiency. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Active Directory Integration: Integrate the RMM platform with Active Directory to automatically discover and manage devices, simplifying user management and device onboarding.
- Ticketing System Integration: Connect the RMM platform to your ticketing system to automate ticket creation, assign tasks, and track resolution progress. This streamlines IT support workflows and improves communication.
- Monitoring Tool Integration: Integrate the RMM platform with your existing monitoring tools to gather comprehensive performance data and proactively identify potential issues. This enables proactive maintenance and reduces downtime.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Integration: Integrate the RMM platform with your SIEM system to correlate security events and identify potential threats. This enhances your security posture and allows for faster incident response.
- Cloud Service Integration: Integrate the RMM platform with cloud services like Office 365 or Google Workspace to manage user accounts, enforce security policies, and monitor cloud usage. This simplifies cloud management and ensures compliance.
Practical Tips for a Successful RMM Platform Implementation
Here are some practical tips to ensure a successful RMM platform implementation:
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Begin with a pilot implementation on a small group of devices or users to test the platform’s functionality and identify any potential issues before full-scale rollout.
- Prioritize User Training: Provide comprehensive training to your IT team on using the RMM platform. Ensure they understand its features, functionalities, and best practices.
- Communicate Effectively: Keep your IT team and stakeholders informed about the implementation process, including timelines, milestones, and any potential disruptions. This builds trust and ensures smooth adoption.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly monitor the platform’s performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure ongoing security updates. This ensures the platform remains effective and efficient over time.
- Seek Vendor Support: Leverage the vendor’s expertise and support resources during the implementation process. They can provide guidance, troubleshooting assistance, and best practices for optimal platform utilization.
RMM Platforms and Remote Work
The rise of remote work has significantly impacted how businesses manage and secure their IT infrastructure. RMM platforms play a crucial role in facilitating remote device management and security, ensuring seamless operations and data protection for distributed workforces.
Facilitating Remote Device Management
RMM platforms empower IT teams to remotely manage and control devices, regardless of their physical location. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with a geographically dispersed workforce.
- Remote Software Installation and Updates: RMM platforms enable IT administrators to install and update software on remote devices, ensuring all systems are running the latest versions and patches. This reduces security vulnerabilities and maintains optimal performance.
- Remote Monitoring and Troubleshooting: RMM solutions provide real-time monitoring of device performance and health. This allows IT teams to identify and resolve issues proactively, minimizing downtime and user disruption. They can also remotely access devices to diagnose and troubleshoot problems, reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Remote Configuration Management: RMM platforms enable centralized configuration management, ensuring consistent settings across all devices. This simplifies policy enforcement and reduces the risk of configuration errors.
- Remote Asset Management: RMM platforms provide a comprehensive inventory of all devices, including hardware and software details. This allows IT teams to track assets, manage licenses, and optimize resource utilization.
Enhancing Remote Security
RMM platforms offer robust security features that protect remote devices and data from threats.
- Endpoint Security: RMM solutions provide endpoint security capabilities, including antivirus protection, malware detection, and firewall management. This helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches on remote devices.
- Data Encryption: RMM platforms enable data encryption on remote devices, safeguarding sensitive information even if the device is lost or stolen.
- Remote Access Control: RMM solutions allow IT teams to control access to remote devices, restricting unauthorized users and preventing data leakage.
- Security Patch Management: RMM platforms automate security patch management, ensuring all devices are up-to-date with the latest security fixes and updates.
Challenges and Opportunities of RMM in Remote Work, Rmm platform
While RMM platforms offer significant advantages for remote work environments, it’s important to consider the challenges and opportunities they present.
- Internet Connectivity: Reliable internet connectivity is crucial for RMM platforms to function effectively. Poor connectivity can lead to delays in data transfer and remote management operations.
- User Privacy: RMM platforms collect data from remote devices, raising concerns about user privacy. Organizations need to implement robust data privacy policies and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating RMM platforms with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging, requiring careful planning and implementation.
- Cost Considerations: RMM platforms can be costly, especially for large organizations with a significant number of remote devices. It’s essential to choose a solution that aligns with the organization’s budget and needs.
Future Trends in RMM
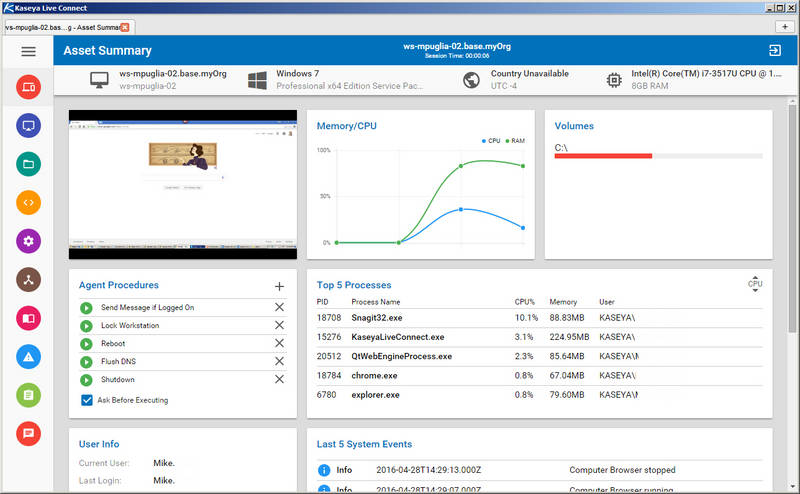
The RMM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Several emerging trends are shaping the future of RMM, promising to enhance efficiency, security, and overall IT management.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are transforming various industries, and RMM is no exception. These technologies are poised to revolutionize how IT professionals manage and secure their networks.
- Automated Incident Response: AI-powered RMM platforms can analyze network data, identify potential threats, and automatically initiate appropriate responses, such as blocking malicious IPs or quarantining infected devices. This automation reduces manual intervention, improves response times, and minimizes the impact of security incidents.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, ML algorithms can predict potential hardware failures before they occur. This allows IT teams to proactively schedule maintenance and prevent downtime, ensuring smooth operations and reducing repair costs.
- Personalized User Experiences: AI-powered RMM platforms can learn user preferences and behaviors, tailoring the interface and features to individual needs. This personalized experience can improve user satisfaction and enhance productivity.
Case Studies of RMM Platform Use

RMM platforms are transforming how IT professionals manage and secure their clients’ systems. Real-world examples showcase the tangible benefits and successful implementation of these platforms.
Benefits of RMM Platforms in Small and Medium Businesses
The adoption of RMM platforms is particularly significant for small and medium businesses (SMBs). These businesses often lack dedicated IT staff, making them susceptible to security vulnerabilities and operational inefficiencies. An RMM platform can address these challenges by providing centralized management, automated tasks, and proactive security measures.
“We were struggling to manage our clients’ systems effectively, with limited resources and a growing workload. Implementing an RMM platform has significantly improved our efficiency, reduced downtime, and allowed us to provide a higher level of service to our clients.” – John, IT Manager at a small business
Case Study: A Healthcare Provider’s Experience with RMM
A healthcare provider with multiple clinics faced challenges in maintaining compliance with HIPAA regulations and managing a distributed IT infrastructure. By implementing an RMM platform, they were able to:
- Centralize patch management, ensuring all devices were updated with the latest security patches, reducing their vulnerability to attacks.
- Automate routine tasks, such as software updates and antivirus scans, freeing up their IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Monitor system performance, identifying and resolving potential issues before they impacted patient care.
- Generate comprehensive reports, demonstrating compliance with HIPAA regulations and providing valuable insights into system performance.
Case Study: A Financial Institution’s Use of RMM for Security
A financial institution implemented an RMM platform to enhance their security posture and protect sensitive customer data. The platform enabled them to:
- Implement endpoint security policies, including real-time threat detection and response, to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Enforce password complexity requirements, reducing the risk of weak passwords and unauthorized access.
- Monitor network traffic, identifying suspicious activity and potential security threats.
- Generate alerts for potential security incidents, enabling them to respond promptly and mitigate risks.
Case Study: A Manufacturing Company’s Experience with RMM for Remote Work
A manufacturing company transitioned to a remote workforce model during the pandemic. An RMM platform played a crucial role in supporting this shift by enabling them to:
- Securely access remote devices, ensuring that employees could work from home without compromising security.
- Provide remote support, resolving technical issues quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime.
- Monitor system performance, ensuring that remote employees had the resources they needed to be productive.
- Enforce security policies, protecting company data and systems from remote threats.
Wrap-Up
In today’s interconnected world, where remote work and hybrid environments are the norm, RMM platforms have become indispensable for businesses of all sizes. They empower IT teams to effectively manage and secure devices, networks, and applications regardless of location, ensuring business continuity and data protection. As technology continues to evolve, RMM platforms will undoubtedly play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of IT management, offering innovative solutions to the ever-growing complexities of the digital landscape.
An RMM platform helps you manage your IT infrastructure efficiently, from monitoring to patching. If you’re looking for ways to optimize your system’s performance, consider using a tool like wise memory optimizer to free up RAM and improve responsiveness.
By optimizing your hardware, you can ensure your RMM platform runs smoothly and effectively.

