Remote network management software has revolutionized the way we manage and monitor our networks. This powerful tool allows IT professionals to remotely access, configure, and troubleshoot network devices from anywhere in the world.
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where you can manage your entire network from your laptop, regardless of your location. This is the reality that remote network management software offers. It empowers IT teams to proactively monitor network performance, identify potential issues before they escalate, and respond quickly to any incidents that arise.
Introduction to Remote Network Management Software
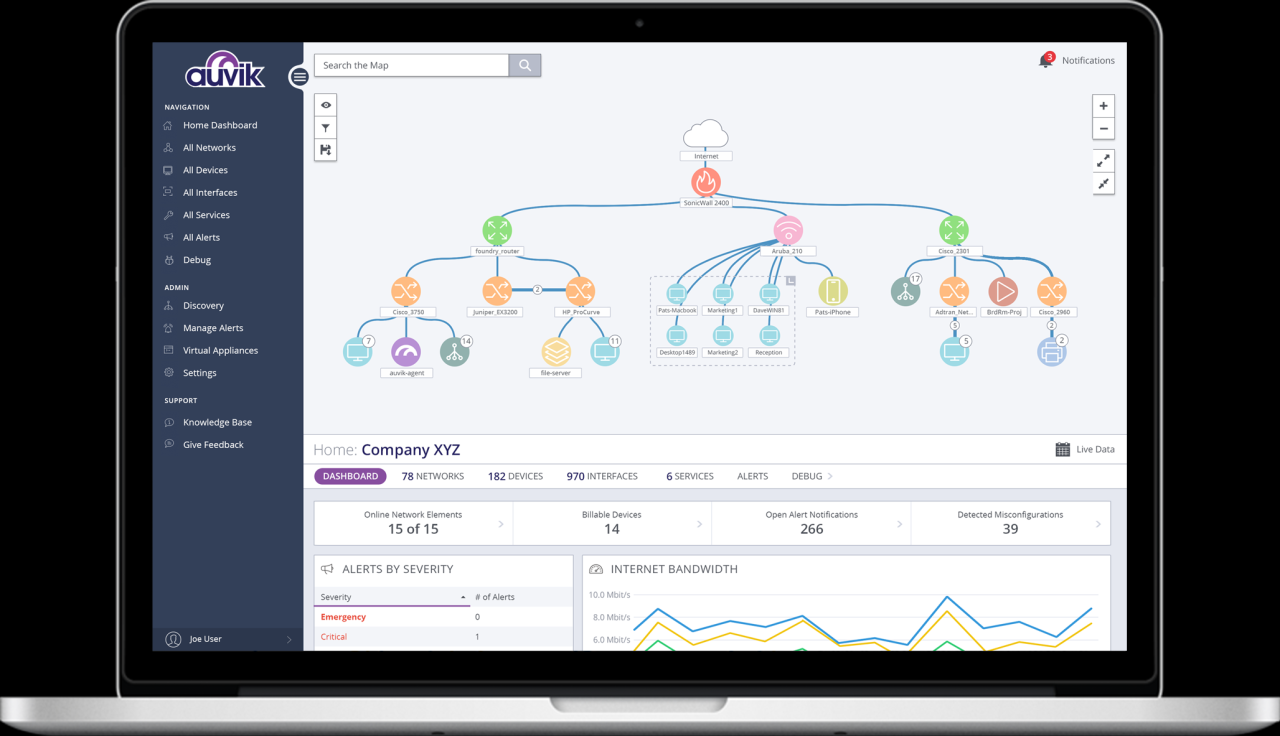
Remote network management software is a powerful tool that enables IT professionals to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot network devices from a remote location. This software provides a centralized platform for managing network infrastructure, streamlining operations, and enhancing network security.
Remote network management software offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced security. By allowing administrators to manage network devices remotely, this software eliminates the need for physical presence, saving time and resources. Additionally, it enables proactive monitoring and troubleshooting, minimizing network disruptions and ensuring optimal performance.
Common Use Cases
Remote network management software finds application in various scenarios across different industries. Here are some common use cases:
- Monitoring Network Performance: Remote network management software provides real-time insights into network performance, enabling administrators to identify bottlenecks, troubleshoot issues, and optimize network utilization.
- Managing Network Devices: From configuring devices to deploying updates and security patches, remote network management software simplifies device management tasks, ensuring consistent and efficient operations.
- Security Management: This software plays a crucial role in securing network infrastructure by providing tools for firewall management, intrusion detection, and vulnerability assessment.
- Troubleshooting Network Issues: Remote network management software offers advanced troubleshooting capabilities, allowing administrators to diagnose and resolve network problems remotely, minimizing downtime and service disruptions.
- Network Automation: Remote network management software enables automation of repetitive tasks, such as device configuration, backup scheduling, and security updates, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Deployment and Implementation
Remote network management software deployment involves selecting the appropriate deployment model and implementing the software effectively. Understanding the different deployment models and the steps involved in implementation is crucial for successful integration into your network infrastructure.
Deployment Models
Deployment models determine how the software is hosted and accessed. Each model offers unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on your specific needs and resources.
- On-premise: The software is installed and managed directly on your own servers within your physical location. This model offers high control and customization but requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT expertise for maintenance.
- Cloud-based: The software is hosted on a third-party cloud provider’s servers, accessible through the internet. This model eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and provides scalability and flexibility, but it might involve concerns about data security and vendor lock-in.
- Hybrid: This model combines elements of both on-premise and cloud-based deployment. You can choose to host certain components on-premise while leveraging the cloud for others. This approach offers flexibility and cost optimization, but it requires careful planning and management to ensure seamless integration.
Implementation Steps
Implementing remote network management software involves a systematic process to ensure smooth integration and optimal performance. The following steps Artikel a general guide for implementation:
- Planning and Assessment: This step involves defining your requirements, identifying existing network infrastructure, and evaluating the software’s capabilities. You should consider factors such as the size and complexity of your network, security requirements, and budget constraints.
- Software Selection and Procurement: Based on your assessment, choose the most suitable software solution that meets your specific needs. Consider factors such as features, pricing, vendor support, and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Installation and Configuration: Once you have procured the software, install it on your servers or cloud platform, following the vendor’s instructions. Configure the software to match your network topology, devices, and security policies.
- Device Integration: Integrate the software with your network devices, such as routers, switches, and firewalls. This step involves configuring device settings to allow communication with the management software.
- User Access and Training: Set up user accounts and permissions for authorized personnel to access the software. Provide training on how to use the software effectively to manage the network.
- Testing and Optimization: Thoroughly test the software’s functionality and performance to ensure it meets your expectations. Make necessary adjustments to optimize performance and address any issues.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Once you are satisfied with the testing results, deploy the software to your production environment. Continuously monitor the software’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
Step-by-Step Guide for Deploying and Configuring Remote Network Management Software
This guide provides a general overview of the steps involved in deploying and configuring remote network management software. The specific steps and configuration options may vary depending on the software you choose.
Step 1: Planning and Assessment
- Define your network management goals and objectives.
- Identify the network devices you need to manage.
- Evaluate your existing network infrastructure and security policies.
- Assess your budget and resources for software procurement and implementation.
Step 2: Software Selection and Procurement
- Research and compare different remote network management software solutions.
- Consider factors such as features, pricing, vendor support, and compatibility with your existing systems.
- Choose the software that best meets your needs and budget.
- Purchase the software licenses and obtain the necessary installation files.
Step 3: Installation and Configuration
- Install the software on your servers or cloud platform, following the vendor’s instructions.
- Configure the software to match your network topology, devices, and security policies.
- Set up user accounts and permissions for authorized personnel.
Step 4: Device Integration
- Configure your network devices to allow communication with the management software.
- This may involve setting up SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) or other protocols.
- Verify that the software can successfully communicate with your devices.
Step 5: Testing and Optimization
- Thoroughly test the software’s functionality and performance.
- Verify that the software can monitor and manage your network devices as expected.
- Make necessary adjustments to optimize performance and address any issues.
Step 6: Deployment and Monitoring
- Deploy the software to your production environment.
- Continuously monitor the software’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Regularly review and update your network management policies and procedures.
Integration and Interoperability: Remote Network Management Software

In today’s complex IT environments, remote network management software needs to seamlessly integrate with other tools and systems to provide a comprehensive and efficient management experience. This integration is crucial for maximizing the benefits of remote network management and streamlining operations.
Interoperability Challenges and Solutions
Interoperability challenges arise when different network management tools and systems are incompatible, hindering data exchange and communication. This can lead to fragmented views of the network, increased complexity, and potential security risks.
- Standardization: Adopting industry standards such as SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and NetFlow helps ensure interoperability between different tools and systems.
- API Integration: Utilizing Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enables seamless data exchange and automation between different software applications.
- Middleware: Middleware solutions can act as a bridge between different systems, facilitating communication and data sharing.
- Open Source Tools: Open source tools often promote interoperability by providing readily available and customizable components that can be integrated with other systems.
Examples of Integration with Existing Systems
Remote network management software can integrate with various existing systems, including:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Integration with SIEM systems allows for centralized security monitoring and incident response, leveraging real-time network data collected by the remote management software.
- Configuration Management Databases (CMDBs): Integration with CMDBs provides a comprehensive view of network devices, configurations, and dependencies, enabling efficient inventory management and change control.
- Ticketing Systems: Integration with ticketing systems allows for automated incident reporting and tracking, streamlining issue resolution and improving communication between IT teams.
- Monitoring and Alerting Systems: Integration with monitoring and alerting systems enables proactive network monitoring, timely notification of issues, and automated remediation actions.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
The effectiveness of remote network management software can be best understood through real-world examples and case studies. These examples showcase how organizations have successfully implemented the software, highlighting the benefits they have reaped and the challenges they encountered during the process.
Impact of Remote Network Management Software on Network Performance and Security
Remote network management software can significantly enhance network performance and security by enabling centralized monitoring, proactive issue detection, and automated troubleshooting. This allows organizations to optimize their network infrastructure, improve uptime, and reduce downtime caused by network issues.
- Improved Network Visibility and Monitoring: Organizations gain comprehensive visibility into their network infrastructure, allowing them to monitor performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and proactively address potential issues. This can lead to a more efficient and reliable network environment. For example, a large retail chain implemented remote network management software to monitor the performance of their point-of-sale systems across multiple locations. The software provided real-time data on system performance, enabling the IT team to identify and resolve issues before they impacted customer service.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Remote network management software enables centralized security management, allowing organizations to implement and enforce consistent security policies across their network. This can help to mitigate security risks and protect sensitive data. For instance, a financial institution deployed remote network management software to centrally manage security policies and monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. The software allowed them to detect and block malicious attacks, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Reduced Downtime and Improved Uptime: By providing real-time insights into network performance and enabling proactive troubleshooting, remote network management software can significantly reduce downtime. This translates to improved business continuity and reduced operational costs. For example, a manufacturing company used remote network management software to monitor the performance of their production line control systems. The software alerted them to potential issues before they caused disruptions, enabling them to resolve them quickly and minimize downtime.
Final Wrap-Up
As technology continues to evolve, remote network management software is becoming increasingly essential for businesses of all sizes. By leveraging the power of automation, advanced analytics, and cloud-based solutions, these tools enable IT teams to optimize network efficiency, enhance security, and ensure business continuity.
Remote network management software empowers IT professionals to oversee and control their network infrastructure from anywhere in the world. This includes the ability to perform critical tasks like device configuration, troubleshooting, and security updates. An integral part of this software is the integration of remote monitoring and management capabilities, which provide real-time insights into network performance and security.
By leveraging these features, organizations can proactively address issues, optimize network efficiency, and ensure business continuity.
