Remote monitoring and management software has revolutionized the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure. This powerful technology empowers organizations to gain real-time visibility into their systems, proactively address issues, and optimize performance from anywhere in the world. By automating routine tasks, simplifying complex processes, and providing comprehensive insights, RMM software helps IT teams enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall security.
Table of Contents
RMM software offers a wide range of features, including endpoint management, patch management, security monitoring, remote control, and reporting and analytics. These capabilities allow businesses to remotely manage and secure their devices, ensure software updates are applied promptly, detect and respond to security threats, troubleshoot issues efficiently, and gain valuable insights into their IT environment.
What is Remote Monitoring and Management Software?
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to manage and monitor their IT infrastructure remotely. This software allows IT professionals to oversee and control various aspects of their network, devices, and applications from a centralized location, streamlining IT operations and improving efficiency.
Key Features and Functionalities of RMM Software
RMM software offers a wide range of features designed to simplify and optimize IT management. These features can be categorized into core functionalities:
- Remote Access and Control: RMM software provides secure remote access to devices, enabling IT professionals to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other tasks remotely. This eliminates the need for physical presence at the device location, saving time and effort.
- System Monitoring: RMM software continuously monitors the health and performance of devices, applications, and networks. It tracks key metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network bandwidth, providing real-time insights into system performance and potential issues.
- Automated Patch Management: Patch management is a crucial aspect of maintaining system security. RMM software automates the process of identifying, downloading, and installing software updates and security patches, ensuring that devices are protected from vulnerabilities and malware.
- Software Deployment: RMM software streamlines software deployment by allowing IT professionals to remotely install and configure applications across multiple devices. This eliminates the need for manual installation and ensures consistency in software configurations.
- Endpoint Security: RMM software plays a critical role in endpoint security by providing features such as antivirus protection, firewall management, and intrusion detection. It helps prevent unauthorized access, malware infections, and other security threats.
- Asset Management: RMM software helps IT professionals manage and track hardware and software assets across the organization. It provides detailed information about each asset, including its configuration, location, and maintenance history.
- Reporting and Analytics: RMM software generates comprehensive reports and analytics on various aspects of IT infrastructure, providing insights into system performance, security posture, and resource utilization. This data helps IT professionals make informed decisions about resource allocation, optimization, and security improvements.
Common RMM Tasks
RMM software empowers IT professionals to perform a wide range of tasks remotely, significantly simplifying and streamlining IT operations. Here are some common examples:
- Patch Management: RMM software automates the process of identifying, downloading, and installing software updates and security patches for all devices within the network. This ensures that devices are protected from vulnerabilities and malware, reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Software Deployment: RMM software allows IT professionals to remotely deploy and configure applications across multiple devices. This eliminates the need for manual installation, saving time and effort, and ensures consistent software configurations.
- Endpoint Security: RMM software provides comprehensive endpoint security features, including antivirus protection, firewall management, and intrusion detection. It helps prevent unauthorized access, malware infections, and other security threats, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining network integrity.
- Troubleshooting and Issue Resolution: RMM software enables IT professionals to remotely access and troubleshoot devices, diagnose issues, and resolve problems quickly and efficiently. This reduces downtime and improves overall system availability.
- Data Backup and Recovery: RMM software can be integrated with backup solutions to automate data backup and recovery processes. This ensures that critical data is protected and can be restored quickly in case of system failures or disasters.
- Remote Monitoring and Alerting: RMM software continuously monitors the health and performance of devices, applications, and networks. It sends alerts to IT professionals when critical events occur, such as system crashes, security breaches, or performance degradation. This allows for prompt intervention and minimizes potential damage.
Benefits of Remote Monitoring and Management: Remote Monitoring And Management Software
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software offers a wide range of advantages for businesses, enabling them to streamline IT operations, improve efficiency, and enhance security.
Improved IT Efficiency
RMM software empowers IT teams to manage and monitor devices remotely, reducing the need for on-site visits and minimizing downtime.
- Automated Patch Management: RMM software automates the process of applying software updates and security patches to all devices, ensuring they are protected against vulnerabilities and remain compliant with industry standards. This reduces the risk of security breaches and minimizes manual effort, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Centralized Management: RMM software provides a centralized platform for managing all IT assets, including computers, servers, and mobile devices. This allows IT teams to monitor system performance, manage user accounts, and deploy software updates from a single console, simplifying administration and improving efficiency.
- Remote Troubleshooting: RMM software enables IT professionals to remotely access and troubleshoot devices, resolving issues quickly and efficiently without the need for physical presence. This reduces downtime and minimizes disruption to users, improving overall productivity.
Reduced Operational Costs
RMM software helps businesses reduce operational costs by automating tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and minimizing downtime.
- Reduced Help Desk Costs: RMM software can automate routine tasks such as password resets and software installations, reducing the workload on help desk staff and freeing them up to handle more complex issues. This can significantly reduce help desk costs and improve overall efficiency.
- Minimized Downtime: RMM software enables proactive monitoring of system performance, allowing IT teams to identify and resolve issues before they escalate and cause downtime. This minimizes disruption to business operations and reduces the cost of downtime.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: RMM software provides insights into IT resource utilization, enabling businesses to optimize resource allocation and reduce unnecessary spending. This can include identifying underutilized servers or applications, allowing businesses to consolidate resources and reduce hardware costs.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
RMM software plays a crucial role in enhancing security and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Real-Time Threat Detection: RMM software provides real-time monitoring of network activity and device behavior, enabling IT teams to detect and respond to security threats promptly. This reduces the risk of data breaches and minimizes the impact of security incidents.
- Automated Security Policies: RMM software enables the automated enforcement of security policies, such as password complexity requirements and access control settings, across all devices. This ensures that all devices are configured securely and comply with industry standards.
- Compliance Reporting: RMM software generates detailed reports on security posture and compliance status, providing evidence to demonstrate compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR. This simplifies compliance audits and reduces the risk of penalties.
Key Features of Remote Monitoring and Management Software
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software offers a range of features that simplify IT management and enhance security. These features can be broadly categorized into endpoint management, patch management, security monitoring, remote control, and reporting and analytics.
Endpoint Management
Endpoint management encompasses all the tools and processes used to manage and control devices connected to a network. RMM software facilitates this by providing a centralized platform for managing multiple endpoints, such as desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices.
- Inventory Management: RMM software automatically discovers and inventories all endpoints on a network, providing a comprehensive overview of hardware and software configurations. This information is crucial for asset management, license compliance, and capacity planning.
- Software Deployment and Management: RMM software enables the deployment and management of software applications across multiple endpoints. This includes installing, updating, and removing software, ensuring consistent software versions and reducing manual effort.
- Configuration Management: RMM software allows for the configuration and standardization of endpoint settings, ensuring consistency across devices and reducing the risk of security vulnerabilities. This includes setting policies for user accounts, network access, and security settings.
Patch Management
Patch management is a critical aspect of IT security, as it involves keeping software and operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. RMM software automates this process, ensuring timely patching and minimizing vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning: RMM software scans endpoints for known vulnerabilities and identifies missing patches. This allows IT teams to prioritize patching efforts and address critical vulnerabilities quickly.
- Automated Patch Deployment: RMM software automates the deployment of patches to endpoints, ensuring timely updates and minimizing downtime. This includes scheduling patch deployments and creating custom patch deployment rules.
- Patch Approval and Reporting: RMM software provides a mechanism for approving patches before deployment and generating reports on patch compliance. This ensures that only approved patches are applied and that patch deployment progress is tracked.
Security Monitoring
Security monitoring is crucial for identifying and responding to security threats. RMM software enhances security monitoring by providing real-time insights into endpoint activity and potential threats.
- Real-time Monitoring: RMM software monitors endpoint activity in real-time, detecting suspicious behavior and potential security breaches. This includes monitoring for malware, unauthorized access, and unusual network activity.
- Threat Detection and Response: RMM software incorporates threat detection and response capabilities, identifying and responding to security threats automatically. This includes blocking malicious traffic, isolating infected endpoints, and launching remediation actions.
- Security Event Logging and Reporting: RMM software logs security events and generates reports, providing a comprehensive view of security incidents and enabling forensic analysis. This information is valuable for identifying patterns, improving security posture, and complying with regulations.
Remote Control
Remote control capabilities allow IT technicians to access and manage endpoints remotely, resolving issues and providing support without physically being present.
- Remote Desktop Access: RMM software provides secure remote desktop access, allowing technicians to control and troubleshoot endpoints remotely. This enables quick resolution of technical issues and reduces the need for onsite visits.
- File Transfer and Management: RMM software enables the transfer of files between endpoints and the central management console. This allows technicians to remotely install software, transfer configuration files, and retrieve data from endpoints.
- Remote Command Execution: RMM software allows technicians to execute commands and scripts remotely on endpoints, automating tasks and streamlining management processes. This includes restarting services, running diagnostic tools, and performing other administrative tasks.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM software provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing IT teams to gain insights into endpoint performance, security posture, and user activity.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting: RMM software monitors endpoint performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space. This data can be used to identify performance bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and improve overall system performance.
- Security Posture Reporting: RMM software generates reports on security posture, including patch compliance, vulnerability status, and threat activity. This information helps IT teams identify security gaps and prioritize remediation efforts.
- User Activity Monitoring and Reporting: RMM software tracks user activity on endpoints, providing insights into user behavior and identifying potential security risks. This information can be used to enforce security policies, monitor compliance, and detect insider threats.
Types of Remote Monitoring and Management Software

Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software is available in various forms, catering to different business needs and organizational sizes. The selection of an RMM solution depends on factors such as the company’s size, industry, budget, and technical expertise.
RMM Solutions for Small Businesses
RMM software designed for small businesses typically offers a streamlined approach to monitoring and managing IT infrastructure. These solutions often feature user-friendly interfaces and simplified functionalities, making them suitable for businesses with limited IT resources.
- Ease of Use: Small business RMM solutions are known for their intuitive interfaces and simplified features, making them accessible even for businesses with limited IT expertise.
- Affordability: These solutions often come with affordable pricing plans, making them budget-friendly for smaller businesses.
- Basic Functionality: They provide essential features such as remote access, patch management, and basic security monitoring.
Examples of RMM solutions for small businesses include:
- Atera: Atera is a cloud-based RMM platform known for its user-friendly interface and affordable pricing. It offers features such as remote access, patch management, and basic security monitoring.
- ConnectWise Manage: ConnectWise Manage is a comprehensive RMM solution that caters to both small and medium-sized businesses. It offers a wide range of features, including remote access, patch management, and security monitoring.
- NinjaRMM: NinjaRMM is another popular RMM solution for small businesses, known for its ease of use and comprehensive feature set. It offers features such as remote access, patch management, and security monitoring.
RMM Solutions for Enterprises
RMM software designed for enterprises typically provides advanced features and functionalities to manage complex IT environments. These solutions are often scalable and customizable, catering to the specific needs of large organizations.
- Scalability: Enterprise RMM solutions are designed to handle large-scale IT infrastructure, with the ability to manage thousands of devices and users.
- Customization: They offer extensive customization options to tailor the solution to the specific requirements of the enterprise.
- Advanced Features: Enterprise RMM solutions provide advanced features such as automation, reporting, and integration with other enterprise systems.
Examples of RMM solutions for enterprises include:
- Datto RMM: Datto RMM is a comprehensive RMM solution designed for enterprise-level IT management. It offers advanced features such as automation, reporting, and integration with other enterprise systems.
- SolarWinds N-central: SolarWinds N-central is another popular enterprise-grade RMM solution. It provides advanced features such as automation, reporting, and security monitoring.
- Kaseya: Kaseya is a leading provider of RMM solutions for enterprises. It offers a wide range of features, including remote access, patch management, and security monitoring.
RMM Solutions for Specific Industries
Certain industries have unique IT requirements, and RMM solutions tailored to these industries can provide specialized features and functionalities. For example, healthcare organizations require RMM solutions that comply with HIPAA regulations, while financial institutions need solutions that meet PCI DSS compliance standards.
- Healthcare: RMM solutions for healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations, ensuring the privacy and security of patient data.
- Finance: RMM solutions for financial institutions must meet PCI DSS compliance standards, safeguarding sensitive financial information.
- Education: RMM solutions for educational institutions need to cater to the specific needs of schools and universities, such as managing student devices and ensuring network security.
Examples of RMM solutions for specific industries include:
- Datto RMM for Healthcare: Datto RMM offers a HIPAA-compliant solution for healthcare organizations, ensuring the security and privacy of patient data.
- SolarWinds N-central for Finance: SolarWinds N-central provides a PCI DSS-compliant solution for financial institutions, protecting sensitive financial information.
- ConnectWise Manage for Education: ConnectWise Manage offers a comprehensive RMM solution for educational institutions, catering to the specific needs of schools and universities.
Choosing the Right Remote Monitoring and Management Software
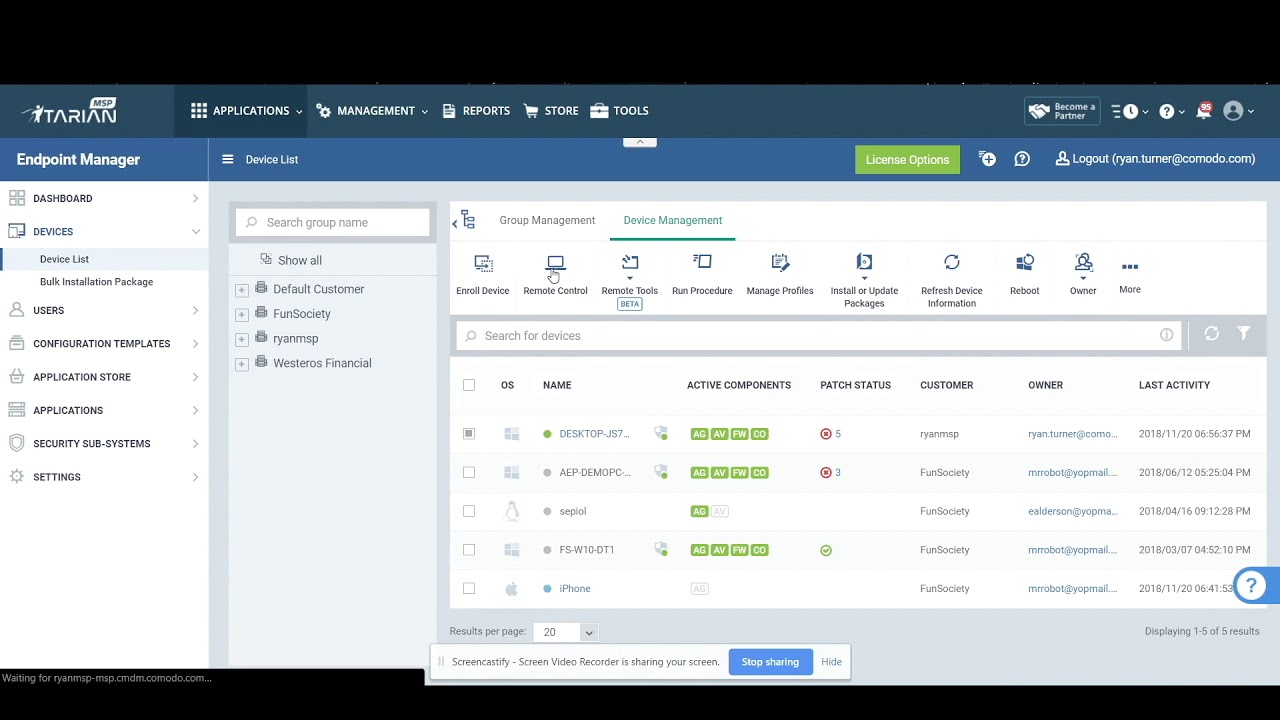
Selecting the appropriate remote monitoring and management (RMM) software is crucial for optimizing IT operations and ensuring the security of your network. The right RMM solution can streamline your workflows, enhance productivity, and provide valuable insights into your IT infrastructure.
Factors to Consider When Selecting RMM Software
To choose the right RMM software, it’s important to consider several factors that align with your specific needs and budget. Here are some key aspects to evaluate:
- Budget: RMM software comes in various price ranges, from affordable options for small businesses to enterprise-grade solutions with advanced features. Determine your budget constraints and find software that offers the necessary features within your financial limits.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your RMM software should be able to scale alongside it. Consider the software’s ability to handle increasing numbers of devices, users, and data. Choose a solution that can adapt to your evolving IT environment.
- Integration with Existing Systems: RMM software should seamlessly integrate with your existing IT infrastructure, such as your help desk, ticketing system, and security tools. Look for solutions that offer robust APIs and integrations to avoid compatibility issues and streamline workflows.
- Ease of Use: RMM software should be user-friendly and intuitive, even for non-technical users. Consider the software’s interface, navigation, and training resources. Choose a solution that minimizes the learning curve and enables efficient management.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential for resolving issues and maximizing your investment in RMM software. Evaluate the provider’s response times, availability, and expertise. Choose a solution with a dedicated support team that can address your technical needs.
Comparing RMM Software Options
Once you’ve identified your key requirements, it’s helpful to compare different RMM software options based on these factors. The following table provides a general overview of the pros and cons of various RMM solutions:
| RMM Software | Budget | Scalability | Integration | Ease of Use | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atera | Affordable | Scalable | Good | Easy | Excellent |
| ConnectWise Automate | Enterprise-grade | Highly Scalable | Extensive | Moderate | Good |
| Datto RMM | Mid-range | Scalable | Good | Moderate | Good |
| NinjaOne | Mid-range | Scalable | Good | Easy | Good |
| SolarWinds MSP | Enterprise-grade | Highly Scalable | Extensive | Moderate | Good |
Implementation and Deployment of Remote Monitoring and Management Software

Implementing and deploying Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software is a crucial step in leveraging its benefits. This process involves a strategic approach to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
Planning and Preparation
Before deploying RMM software, it’s essential to plan and prepare for a smooth transition. This involves:
- Defining Scope and Objectives: Clearly define the scope of RMM implementation, including the target endpoints, specific tasks to be automated, and desired outcomes.
- Identifying Resources: Determine the necessary resources, such as technical personnel, budget, and time required for successful implementation.
- Selecting RMM Software: Choose an RMM solution that aligns with your specific needs and organizational infrastructure.
- Training and Documentation: Provide training for IT staff on using the RMM software and create comprehensive documentation for reference and future troubleshooting.
Configuration and Deployment
Once you have chosen your RMM software, you need to configure and deploy it on your endpoints. Here are the key steps:
- Agent Installation: Install the RMM agent on each endpoint. This can be done manually or through a centralized deployment mechanism.
- Policy Configuration: Configure security policies, update schedules, and other settings within the RMM console to align with your organization’s security standards.
- Endpoint Management: Use the RMM software to manage and monitor endpoints, including software updates, patch management, and security configurations.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrate the RMM software with your existing IT infrastructure, such as Active Directory, ticketing systems, and monitoring tools.
Best Practices for RMM Implementation, Remote monitoring and management software
To ensure a successful RMM implementation, follow these best practices:
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Begin by implementing RMM on a small group of endpoints and gradually expand as you gain experience.
- Test Thoroughly: Conduct thorough testing before deploying RMM to the entire organization to identify and resolve any issues.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of the RMM software and make adjustments as needed.
- Provide User Support: Offer adequate user support for IT staff and end-users to address any questions or issues.
- Keep It Updated: Regularly update the RMM software and agents to ensure optimal performance and security.
Troubleshooting and Support
During RMM implementation, you may encounter challenges. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check Agent Connectivity: Ensure the RMM agent is properly connected to the central server.
- Review Logs and Error Messages: Analyze the logs and error messages for insights into any issues.
- Contact Support: If you are unable to resolve the issue, contact the RMM vendor’s support team for assistance.
Security Considerations
RMM software can enhance security but also presents potential security risks. Consider these factors:
- Data Security: Ensure the RMM software has robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Access Control: Implement strong access control mechanisms to restrict access to the RMM console.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly scan for vulnerabilities in the RMM software and agents.
Cost-Effectiveness
RMM software can help organizations save costs by automating tasks and reducing downtime. However, it’s crucial to:
- Evaluate ROI: Calculate the return on investment (ROI) to ensure the benefits outweigh the costs.
- Optimize Resource Utilization: Use the RMM software to optimize resource utilization and minimize unnecessary spending.
Security Considerations for Remote Monitoring and Management
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software offers significant advantages for businesses, but it also introduces security risks that must be carefully addressed. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures is crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of your systems.
Potential Security Risks Associated with RMM Software
RMM software provides remote access to your systems, which inherently creates security vulnerabilities.
- Unauthorized Access: Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in the RMM software or its infrastructure to gain unauthorized access to your systems, potentially stealing data or installing malware.
- Data Breaches: If the RMM software itself is compromised, attackers could access sensitive data stored on your systems, including customer information, financial records, and proprietary data.
- Denial-of-Service Attacks: Attackers could target the RMM software or its infrastructure to disrupt your operations by causing system outages or slowdowns.
- Data Manipulation: Hackers could modify or delete data on your systems, potentially causing financial losses or operational disruptions.
Best Practices for Securing RMM Software and Protecting Sensitive Data
To mitigate security risks associated with RMM software, it is essential to adopt best practices for securing your systems and data.
- Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication for all user accounts associated with the RMM software. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their mobile device.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update the RMM software and its underlying operating system to patch vulnerabilities and ensure you have the latest security features. This is crucial for staying ahead of potential exploits and mitigating risks.
- Limit User Permissions: Assign the least privileges necessary to each user to access and manage systems through the RMM software. This principle of least privilege helps to restrict unauthorized access and minimize potential damage in case of a security breach.
- Encrypt Data in Transit and at Rest: Implement strong encryption for data transmitted between your systems and the RMM software, as well as for data stored on your systems. This helps to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access even if the data is intercepted during transmission or if the systems are compromised.
- Monitor Activity and Logs: Regularly monitor user activity and system logs for suspicious behavior or potential security breaches. This proactive approach allows you to identify and address security threats promptly, reducing the impact of potential incidents.
Importance of Regular Security Audits and Updates for RMM Systems
Regular security audits and updates are crucial for maintaining the security of your RMM systems.
- Security Audits: Periodic security audits help to identify vulnerabilities in your RMM software and infrastructure. These audits should be conducted by qualified security professionals who can assess your security posture and recommend improvements.
- Regular Updates: Updating the RMM software and its underlying operating system is essential for patching vulnerabilities and ensuring you have the latest security features. This should be done regularly and in a timely manner to stay ahead of potential exploits and mitigate risks.
Real-World Examples of Remote Monitoring and Management Software in Action
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes, enabling them to streamline IT operations, improve security, and enhance overall efficiency. By leveraging the power of RMM solutions, organizations can gain valuable insights into their IT infrastructure, proactively address potential issues, and optimize their technology investments.
Examples of RMM Software Use Cases
RMM software offers a wide range of applications, empowering businesses to address various challenges and achieve specific goals. Here are some real-world examples of how organizations are using RMM software to improve their IT operations:
- Proactive Maintenance and Patch Management: A healthcare provider with multiple clinics across a region implemented an RMM solution to automate patch management and software updates for all devices. This ensured that all systems were up-to-date with the latest security patches, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and data breaches. The RMM software also monitored system performance, identifying potential issues before they impacted patient care.
- Remote Support and Troubleshooting: A financial services company with a distributed workforce adopted an RMM solution to provide remote support to employees working from home. The software enabled IT technicians to remotely access and troubleshoot devices, ensuring that employees had the necessary support to maintain productivity. This reduced the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources.
- Security Monitoring and Incident Response: A retail chain with numerous stores nationwide implemented an RMM solution to monitor security events across its entire network. The software detected suspicious activity, such as malware infections or unauthorized access attempts, allowing security teams to respond quickly and mitigate potential threats. This helped to protect sensitive customer data and ensure business continuity.
- Asset Management and Inventory Control: A manufacturing company with a complex IT infrastructure leveraged an RMM solution to manage its hardware and software assets. The software provided detailed inventory information, including asset details, licensing information, and maintenance schedules. This enabled the company to optimize asset utilization, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with licensing agreements.
Concluding Remarks
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for robust and efficient remote monitoring and management solutions will only increase. By embracing RMM software, businesses can streamline their IT operations, improve security posture, and unlock new levels of productivity. Whether it’s managing a small business network or overseeing a large enterprise infrastructure, RMM software provides the tools and insights needed to thrive in today’s dynamic IT landscape.
Remote monitoring and management software empowers you to oversee your systems from anywhere, ensuring optimal performance. A crucial component of many systems is the media encoder , which converts media files into different formats for various platforms. By integrating remote monitoring capabilities with your media encoding workflow, you can proactively identify and resolve issues, guaranteeing a seamless and efficient media delivery process.

