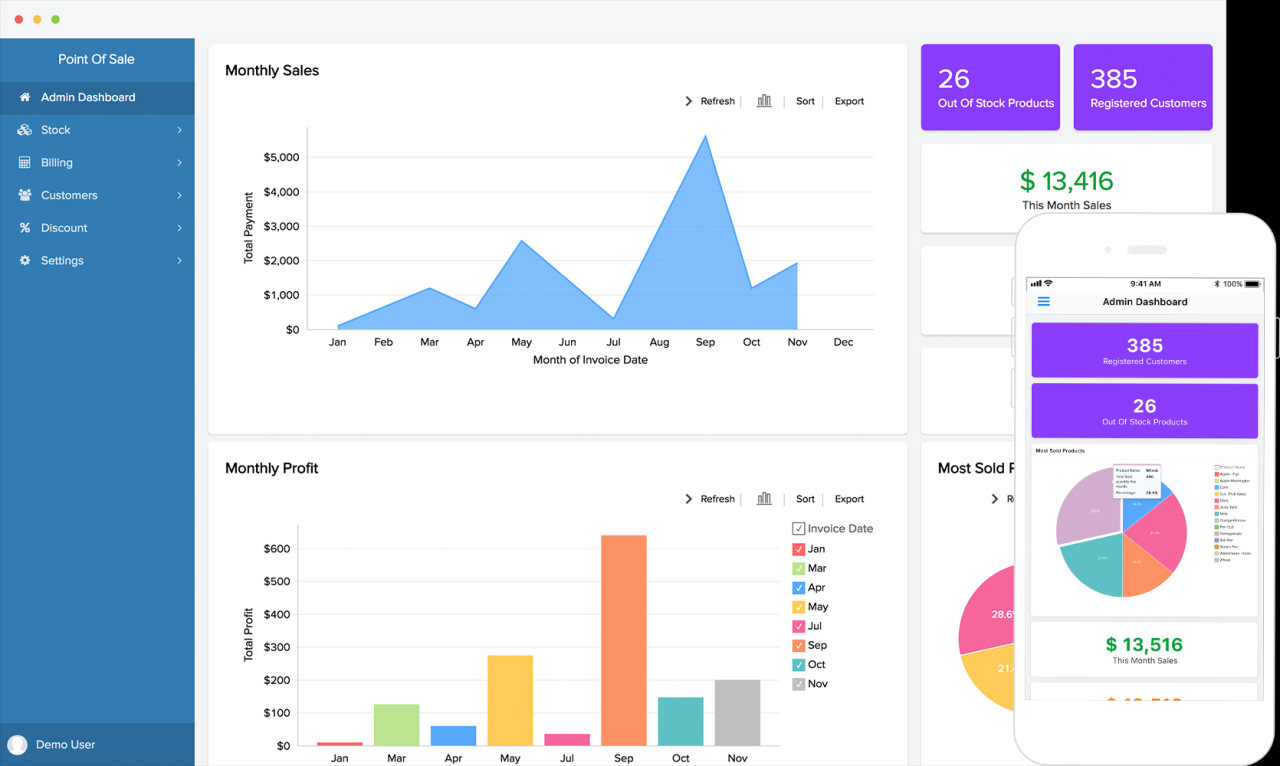
POS Dashboard, a powerful tool for modern businesses, provides a centralized view of your operations, giving you real-time insights into sales, inventory, customer behavior, and more. Imagine having a crystal ball that reveals the heartbeat of your business, allowing you to make informed decisions and optimize performance in a dynamic marketplace.
Table of Contents
A POS dashboard serves as a command center, consolidating data from various sources like point-of-sale systems, inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and accounting software. This unified platform empowers you to understand your business’s performance, identify trends, and make strategic adjustments to stay ahead of the competition.
What is a POS Dashboard?
A POS dashboard is a powerful tool that provides a centralized view of key performance indicators (KPIs) related to your point-of-sale (POS) system. It allows businesses to monitor and analyze sales data, inventory levels, customer behavior, and other vital metrics in real-time, enabling informed decision-making and optimized business operations.
Key Components of a POS Dashboard
The components of a POS dashboard vary depending on the specific software and the needs of the business. However, common elements include:
- Sales Performance: This section typically displays real-time sales data, including total sales, average transaction value, sales by product category, and sales by employee. It helps businesses track their revenue, identify trends, and monitor the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Inventory Management: This component provides insights into inventory levels, stock turnover rates, and low-stock alerts. It helps businesses optimize inventory management, reduce waste, and ensure that popular items are always in stock.
- Customer Analytics: This section offers insights into customer demographics, purchase history, and loyalty program participation. It helps businesses understand their customer base, tailor marketing efforts, and improve customer retention.
- Employee Performance: This component tracks employee sales, transaction speed, and customer satisfaction ratings. It allows businesses to monitor employee performance, identify areas for improvement, and reward top performers.
- Financial Reports: This section provides detailed financial reports, including profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It helps businesses understand their financial health, track expenses, and make informed financial decisions.
Benefits of Using a POS Dashboard
POS dashboards offer numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes, including:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing real-time insights into key business metrics, POS dashboards enable businesses to make data-driven decisions that can optimize operations and drive revenue growth.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: POS dashboards can help businesses identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and streamline operations, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: By providing insights into customer behavior, POS dashboards allow businesses to personalize their offerings, improve customer service, and build stronger relationships with their customers.
- Improved Profitability: By tracking key financial metrics and identifying areas for improvement, POS dashboards can help businesses increase profitability and maximize their return on investment.
- Enhanced Business Intelligence: POS dashboards provide a centralized platform for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing business data, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights and make strategic decisions.
Types of POS Dashboards
POS dashboards come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and functionalities. Understanding these types helps businesses choose the right dashboard to optimize their operations.
Basic POS Dashboards
Basic POS dashboards provide a fundamental overview of key performance indicators (KPIs). They typically display real-time sales data, inventory levels, and customer activity. These dashboards are often included in basic POS systems and are suitable for small businesses with simple reporting requirements.
- Features: Real-time sales data, inventory levels, customer activity, basic reports.
- Industries: Retail, restaurants, small businesses.
- Pros: Easy to use, affordable, provide essential insights.
- Cons: Limited customization, lack of advanced analytics, may not be suitable for complex operations.
Advanced POS Dashboards
Advanced POS dashboards offer more comprehensive data visualization and analysis capabilities. They go beyond basic reporting and provide insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and operational efficiency. These dashboards are often used by larger businesses and those with more complex operations.
- Features: Detailed sales data, customer segmentation, inventory management, employee performance tracking, advanced reporting, customizable dashboards.
- Industries: Retail, restaurants, hospitality, e-commerce.
- Pros: Comprehensive data analysis, customizable dashboards, support for multiple data sources, actionable insights.
- Cons: More complex to set up and use, higher cost, may require technical expertise.
Industry-Specific POS Dashboards
Industry-specific POS dashboards are tailored to the unique needs of particular sectors. For example, a restaurant POS dashboard may focus on table management, order tracking, and kitchen efficiency, while a retail POS dashboard might emphasize customer loyalty programs and inventory optimization.
- Features: Industry-specific KPIs, tailored reports, integration with industry-specific tools.
- Industries: Retail, restaurants, hospitality, healthcare, education.
- Pros: Highly relevant insights, improved operational efficiency, better customer experience.
- Cons: May be less flexible for businesses operating in multiple industries, higher cost.
Key Metrics and Data Points
A POS dashboard provides a comprehensive view of your business’s performance, offering valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and operational efficiency. By monitoring key metrics and data points, you can make informed decisions to optimize your business strategies and drive growth.
Sales Performance
Sales performance metrics provide insights into your business’s revenue generation. Understanding these metrics helps you identify growth opportunities, address sales bottlenecks, and optimize your pricing strategies.
- Total Revenue: This metric reflects the overall income generated from sales. Analyzing total revenue trends over time can reveal growth patterns, seasonal fluctuations, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Average Transaction Value (ATV): This metric represents the average amount spent by customers per transaction. A higher ATV indicates customers are purchasing more items or higher-priced products. It can be influenced by factors like product pricing, promotions, and upselling strategies.
- Sales by Product Category: This metric breaks down sales by product category, revealing the popularity of different product lines. This information is crucial for inventory management, product development, and marketing efforts.
- Sales by Employee: This metric tracks sales generated by individual employees. Analyzing this data can identify top performers, identify areas for training, and assess employee performance.
Customer Behavior
Understanding customer behavior is crucial for building customer loyalty, driving repeat purchases, and tailoring your marketing efforts.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric represents the average cost incurred to acquire a new customer. Analyzing CAC helps you evaluate the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns and identify cost-effective acquisition channels.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This metric estimates the total revenue generated from a single customer over their entire relationship with your business. A higher CLTV indicates customer loyalty and repeat purchases, contributing to long-term business growth.
- Average Order Frequency: This metric measures the average number of orders placed by customers over a specific period. It indicates customer engagement and the effectiveness of your retention strategies.
- Customer Retention Rate: This metric represents the percentage of customers who return to make repeat purchases. A high retention rate suggests customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to sustainable business growth.
Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency metrics provide insights into your business’s operational processes, highlighting areas for improvement and optimization.
- Inventory Turnover Rate: This metric measures the rate at which inventory is sold and replenished. A high turnover rate indicates efficient inventory management and minimizes the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
- Labor Cost: This metric represents the percentage of revenue spent on employee wages and benefits. Analyzing labor cost helps you identify areas for optimization, such as streamlining processes or reducing staff overtime.
- Transaction Speed: This metric measures the average time it takes to complete a transaction. A shorter transaction time indicates efficient checkout processes and customer satisfaction.
- Number of Returns: This metric tracks the number of returned items. A high return rate can indicate issues with product quality, inaccurate product descriptions, or poor customer service.
Financial Performance
Financial performance metrics provide a comprehensive view of your business’s financial health, highlighting profitability, cash flow, and overall financial stability.
- Gross Profit Margin: This metric represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold. A higher gross profit margin indicates strong pricing strategies and efficient cost management.
- Net Profit Margin: This metric reflects the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses, including operating costs and taxes. A higher net profit margin indicates strong profitability and financial stability.
- Cash Flow: This metric tracks the movement of cash into and out of your business. A positive cash flow indicates sufficient funds to meet operational needs and invest in growth opportunities.
- Working Capital: This metric represents the difference between current assets and current liabilities. A healthy working capital ensures sufficient liquidity to meet short-term financial obligations.
Data Interpretation and Analysis
Interpreting and analyzing data presented on a POS dashboard is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Trends and Patterns: Look for trends and patterns in data over time, such as seasonal fluctuations, growth trends, or declines. This information can help you identify opportunities and address challenges.
- Benchmarking: Compare your performance metrics to industry benchmarks or competitors to understand your position relative to the market.
- Root Cause Analysis: Investigate the root causes of significant deviations from expected performance. This can involve identifying factors like product launches, marketing campaigns, or operational changes that impact your business.
- Actionable Insights: Use data analysis to identify actionable insights that can improve your business performance. For example, you can identify underperforming products, optimize marketing campaigns, or streamline operational processes.
Dashboard Design and Layout
A well-designed POS dashboard is crucial for effective business insights and decision-making. It should present data clearly, efficiently, and in a way that is easy to understand and act upon.
Dashboard Design Principles and Best Practices
Effective dashboard design prioritizes clarity, conciseness, and visual appeal. Key principles include:
- Focus on Key Metrics: Prioritize the most critical performance indicators, ensuring the dashboard highlights the most important data points for your business goals.
- Visual Hierarchy: Use color, size, and placement to guide the user’s eye towards the most important information. For instance, larger font sizes or bolder colors can emphasize critical metrics.
- Consistent Design: Maintain a consistent visual style throughout the dashboard, including color schemes, fonts, and chart types. This promotes a cohesive and professional look.
- Data Visualization: Employ appropriate chart types to represent data effectively. Bar charts are suitable for comparisons, while line charts are ideal for trends over time. Pie charts illustrate proportions, and scatter plots show relationships between variables.
- Interactive Elements: Consider incorporating interactive elements, such as drill-down capabilities, to allow users to explore data in more detail.
- User-Friendly Navigation: Ensure the dashboard is easy to navigate, with clear labels and intuitive controls. Users should be able to find the information they need quickly and effortlessly.
Effective POS Dashboard Layouts
Effective dashboard layouts typically follow a structure that emphasizes clarity and ease of understanding. Common approaches include:
- Card-Based Layout: This approach utilizes individual cards to display specific metrics, often with a combination of text and visualizations. It allows for easy scanning and comparison of different data points.
- Grid Layout: A grid layout arranges information in rows and columns, creating a structured and organized appearance. This approach is well-suited for displaying multiple metrics or data sets.
- Storytelling Layout: This approach uses a narrative structure to guide users through the data, highlighting key insights and trends. It often combines visualizations with textual explanations and calls to action.
User-Friendliness and Data Visualization
A user-friendly POS dashboard is essential for maximizing its value. It should be designed with the user’s needs in mind, considering their level of technical expertise and the information they require.
- Intuitive Interface: The dashboard should be easy to navigate and understand, with clear labels and controls. Avoid technical jargon and complex terminology.
- Visual Appeal: A visually appealing dashboard can make data more engaging and easier to comprehend. Use colors, shapes, and animations strategically to enhance the user experience.
- Accessibility: Ensure the dashboard is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities. Consider factors such as color contrast, font size, and keyboard navigation.
Real-Time Data and Analytics: Pos Dashboard
Real-time data is the lifeblood of a successful POS dashboard. It provides a constant stream of up-to-the-minute information about your business operations, enabling you to make informed decisions and optimize performance.
The Importance of Real-Time Data
Real-time data empowers businesses to gain a clear and immediate understanding of their current state, allowing them to respond swiftly to changing market dynamics and customer demands. This is especially crucial in today’s fast-paced retail environment, where customer expectations are constantly evolving.
How Real-Time Data Aids Decision Making
Real-time data provides valuable insights that can help businesses make informed decisions in several ways:
- Inventory Management: Real-time inventory data helps businesses track stock levels, identify potential shortages, and optimize replenishment strategies, ensuring that products are available when customers need them.
- Sales Performance Analysis: Real-time sales data provides a clear picture of sales trends, customer behavior, and product popularity. This information allows businesses to identify best-selling items, adjust pricing strategies, and target marketing efforts effectively.
- Customer Service Optimization: Real-time data can track customer wait times, identify areas for improvement in customer service, and help businesses respond to customer inquiries quickly and efficiently.
- Fraud Detection: Real-time transaction data can be analyzed to detect suspicious activity and prevent fraudulent transactions, safeguarding businesses from financial losses.
Data Analytics in Real-Time
Data analytics plays a crucial role in extracting valuable insights from real-time data. By applying statistical models, machine learning algorithms, and other analytical techniques, businesses can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in the data.
Data Analytics Applications, Pos dashboard
Data analytics can be used to:
- Predict future sales: Businesses can use historical sales data and real-time trends to predict future sales and adjust their inventory and marketing strategies accordingly.
- Optimize pricing: Real-time data can be used to analyze customer price sensitivity and competitor pricing, allowing businesses to optimize their pricing strategies for maximum profitability.
- Personalize customer experiences: By analyzing customer purchase history and preferences, businesses can personalize marketing messages, product recommendations, and customer service interactions.
- Improve operational efficiency: Data analytics can be used to identify bottlenecks in operations, optimize staffing levels, and streamline processes for increased efficiency.
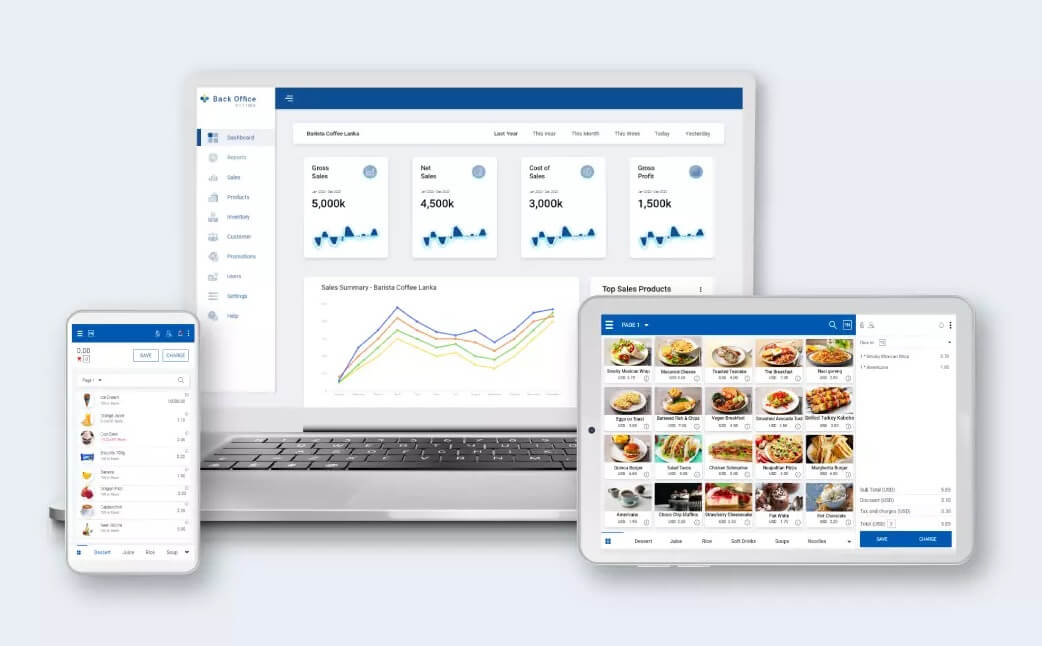
Integration with Other Systems
POS dashboards are designed to be more than just standalone tools; they thrive when connected to other business systems, forming a powerful network that streamlines operations and unlocks valuable insights. This integration fosters a seamless flow of data, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors, ultimately leading to better decision-making and enhanced efficiency.
Benefits of Seamless Integration
Seamless integration between a POS dashboard and other systems offers numerous benefits, enhancing data flow and streamlining business operations.
- Real-time Data Visibility: Integration allows for real-time data exchange between systems, providing a unified view of business operations. This enables businesses to track inventory levels, customer interactions, and financial performance in real-time, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Automated Data Synchronization: Eliminates manual data entry and reconciliation, reducing the risk of errors and saving time. Data is automatically updated across systems, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
- Improved Business Intelligence: Integration provides a holistic view of business data, allowing for more comprehensive analysis and identification of trends and patterns. This empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions across all departments.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Integrated systems allow businesses to provide a more personalized and seamless customer experience. For example, CRM integration enables businesses to access customer purchase history and preferences, leading to targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer service.
Common Integrations and Functionalities
POS dashboards can integrate with various business systems, each offering unique functionalities. Here are some common integrations:
- Inventory Management Systems: Integration with inventory management systems provides real-time inventory visibility, allowing businesses to track stock levels, reorder points, and manage inventory efficiently. This reduces stockouts and overstocking, optimizing inventory costs and maximizing profitability.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Integration with CRM systems allows businesses to track customer interactions, purchase history, and preferences. This information can be used to personalize marketing campaigns, provide targeted customer service, and build stronger customer relationships.
- Accounting Software: Integration with accounting software streamlines financial reporting and reconciliation. Transactions recorded in the POS system are automatically reflected in the accounting software, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors. This provides accurate financial insights and simplifies financial management.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Integration with email marketing platforms allows businesses to send targeted email campaigns based on customer purchase history and preferences. This improves marketing effectiveness and drives sales by reaching the right customers with the right message at the right time.
- Loyalty Programs: Integration with loyalty programs allows businesses to track customer loyalty points and reward their most valuable customers. This encourages repeat business and builds customer loyalty.
Examples of Integrations
- Shopify and Square: Shopify, an e-commerce platform, integrates with Square, a POS system, enabling businesses to manage both online and in-store sales from a single platform. This integration provides a unified view of customer data, inventory levels, and sales performance across all channels.
- QuickBooks and Xero: QuickBooks and Xero, popular accounting software, integrate with various POS systems, automating financial reporting and reconciliation. This simplifies financial management and provides real-time insights into business performance.
- Mailchimp and Salesforce: Mailchimp, an email marketing platform, integrates with Salesforce, a CRM system, allowing businesses to personalize email campaigns based on customer data and purchase history. This enhances marketing effectiveness and improves customer engagement.
Security and Data Privacy
A POS dashboard holds sensitive customer and financial data, making security and data privacy paramount. Robust security measures are essential to safeguard this information from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential misuse.
Data Encryption
Data encryption is a crucial aspect of POS dashboard security. Encrypting sensitive data, such as customer credit card information and transaction details, ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot decipher it without the decryption key.
- Encryption in Transit: This involves encrypting data while it is being transmitted between the POS system and the dashboard, protecting it from interception during network communication.
- Encryption at Rest: This ensures that data stored on the dashboard’s servers is encrypted, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users even if the server is compromised.
Access Control and Authentication
Implementing robust access control measures and multi-factor authentication are vital for protecting POS dashboard data.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): This approach assigns different levels of access to users based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization. For example, a cashier may only have access to transaction details, while a manager may have access to sales reports and inventory data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This involves requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access to the dashboard. This can include a password, a one-time code sent to their phone, or biometric authentication.
Regular Security Audits and Updates
Regular security audits and software updates are essential to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Security Audits: These involve comprehensive assessments of the dashboard’s security posture, including network security, access controls, and data encryption protocols.
- Software Updates: Regularly updating the POS dashboard software ensures that the system is protected against the latest security threats and vulnerabilities.
Data Backup and Recovery
Implementing a robust data backup and recovery plan is crucial for mitigating data loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or other unforeseen events.
- Regular Backups: Regularly backing up the POS dashboard data ensures that even if the primary data is lost, a recent copy is available for restoration.
- Off-Site Storage: Storing backups in a separate location, such as a cloud storage service, provides an additional layer of protection against data loss due to local disasters.
Data Retention Policies
Establishing clear data retention policies helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations and minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Data Minimization: Organizations should only collect and store data that is absolutely necessary for their business operations. This reduces the amount of sensitive data that needs to be protected.
- Data Deletion: Data retention policies should specify how long data is retained and when it should be deleted. This helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Employee Training and Awareness
Training employees on data security best practices is essential for protecting sensitive data.
- Security Awareness Training: Employees should be educated on the importance of data security, how to identify phishing attempts, and the proper handling of sensitive information.
- Password Management: Employees should be trained on the importance of strong passwords and how to create and manage them securely.
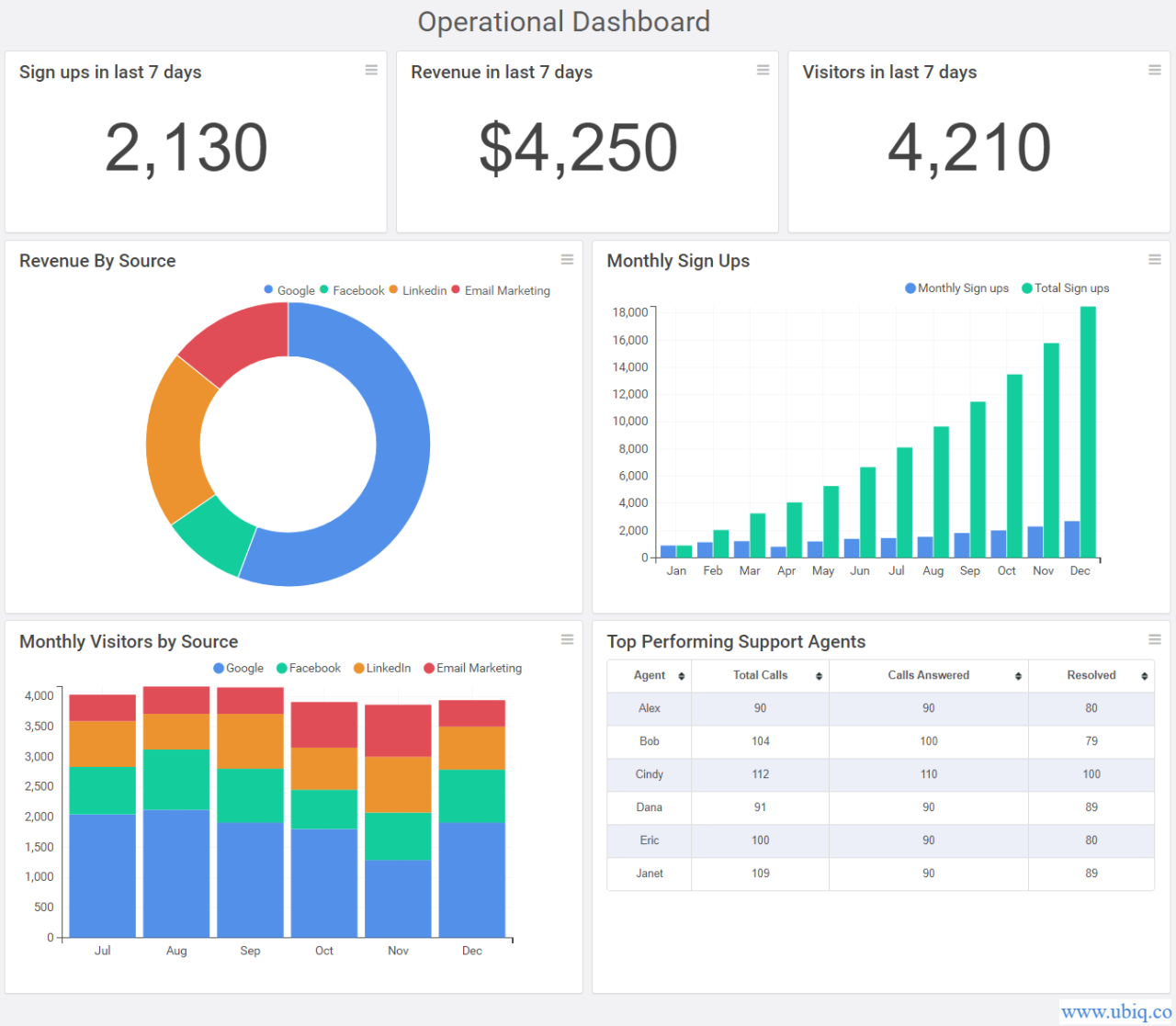
Reporting and Insights
POS dashboards are not just about displaying real-time data; they are powerful tools for generating insightful reports that help businesses understand their performance and make informed decisions. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of various aspects of the business, enabling them to track progress, identify trends, and optimize operations.
Types of Reports
POS dashboards generate a variety of reports to cater to different business needs. These reports can be customized to focus on specific areas of interest and can be easily shared with stakeholders for analysis and decision-making. Here are some common types of reports generated by POS dashboards:
- Sales Reports: These reports provide detailed information about sales performance, including total sales, average transaction value, top-selling products, and sales by time period. They help businesses track revenue growth, identify popular products, and analyze customer buying patterns.
- Inventory Reports: Inventory reports track stock levels, monitor inventory turnover rates, identify slow-moving items, and provide insights into inventory management practices. They help businesses optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce storage costs.
- Customer Reports: These reports provide insights into customer behavior, such as customer demographics, purchase history, and loyalty program engagement. They help businesses understand their customer base, target specific segments, and personalize marketing campaigns.
- Employee Reports: Employee reports track employee performance, such as sales figures, customer satisfaction ratings, and time spent on tasks. They help businesses identify top performers, recognize areas for improvement, and optimize staffing levels.
- Financial Reports: Financial reports provide a comprehensive overview of the business’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profit margins, and cash flow. They help businesses track financial health, identify areas for cost optimization, and make informed financial decisions.
Tracking Performance and Identifying Trends
Reports generated by POS dashboards play a crucial role in tracking business performance and identifying trends. By analyzing data over time, businesses can gain insights into how their operations are performing and identify areas for improvement. For example, a sales report that shows a consistent decline in sales over several months could indicate a need to review pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, or product offerings.
Extracting Valuable Insights
Extracting valuable insights from reports requires careful analysis and interpretation. Businesses can use various techniques to analyze report data, such as:
- Data Visualization: Visualizing data through charts, graphs, and dashboards can help businesses quickly identify patterns and trends that might be missed in raw data.
- Trend Analysis: Analyzing data over time can reveal trends in sales, inventory, customer behavior, and other key metrics. This helps businesses anticipate future performance and make proactive adjustments.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing data across different time periods, locations, or product categories can provide valuable insights into performance differences and identify areas for improvement.
- Statistical Analysis: Using statistical tools and techniques can help businesses identify statistically significant trends and patterns in data, providing a more robust understanding of business performance.
User Roles and Permissions
A POS dashboard is typically accessed by various individuals with different levels of responsibility and authority. Implementing a robust user role and permission system is crucial for maintaining data security, ensuring operational efficiency, and preventing unauthorized access.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a fundamental security principle that defines access levels based on the roles assigned to users. It provides a structured approach to managing user permissions, ensuring that individuals have access only to the data and functionalities they need to perform their assigned tasks.
- RBAC streamlines user management by grouping users into roles with predefined permissions.
- It reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by limiting user access to specific data and functionalities.
- RBAC simplifies administration by eliminating the need to individually assign permissions to each user.
User Roles and Permissions
Here are some common user roles in a POS dashboard environment and their associated permissions:
- Administrator: The administrator has full access to all features and data within the POS dashboard. They can create, edit, and delete user accounts, manage roles and permissions, configure system settings, and access all reports and analytics. This role is typically reserved for system administrators or high-level managers.
- Manager: Managers have access to specific data and functionalities relevant to their departments or areas of responsibility. They can view sales reports, track inventory levels, manage employee schedules, and access other data related to their assigned tasks. They may have limited permissions to modify data or system settings.
- Cashier: Cashiers have limited access to the POS dashboard, primarily focused on processing transactions. They can access customer information, view product details, and enter sales data. They typically have restricted access to reports, analytics, and system settings.
- Sales Representative: Sales representatives have access to customer information, sales history, and product details. They can track their sales performance, view customer profiles, and generate sales reports. They may have limited access to inventory management or other administrative functionalities.
Future Trends in POS Dashboards
The retail landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. As a result, POS dashboards are also undergoing significant transformations, incorporating innovative features and functionalities to meet the evolving needs of businesses.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly transforming various industries, and retail is no exception. POS dashboards are increasingly integrating AI capabilities to enhance decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and personalize customer experiences. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from POS systems, customer interactions, and market trends to provide valuable insights and predictions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI-powered predictive analytics can help businesses forecast demand, optimize inventory levels, and anticipate customer needs. By analyzing historical sales data, customer behavior, and external factors, AI models can generate accurate forecasts, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about inventory management, pricing, and promotions. For example, a clothing retailer could use AI to predict the demand for specific clothing items based on seasonal trends, weather patterns, and social media buzz.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI can personalize the customer experience by recommending products or services based on individual preferences and past purchase history. By analyzing customer data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and preferences, enabling businesses to offer tailored recommendations that increase customer satisfaction and drive sales. For example, a grocery store could use AI to recommend products based on a customer’s past purchases, dietary restrictions, or allergies.
- Fraud Detection: AI can help businesses detect fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual patterns in POS data. By analyzing transaction history, customer behavior, and other relevant data, AI models can flag suspicious activities, reducing the risk of financial losses. For example, a bank could use AI to detect fraudulent credit card transactions by identifying unusual spending patterns or transactions originating from unusual locations.
Closure
By embracing a POS dashboard, businesses gain a competitive edge through data-driven insights, streamlined operations, and improved customer experiences. The ability to monitor key metrics, analyze trends, and adapt to changing market conditions is crucial for success in today’s fast-paced environment. A POS dashboard empowers businesses to move beyond reactive decision-making and embrace proactive strategies that drive growth and profitability.
POS dashboards are essential tools for businesses, providing real-time insights into sales, inventory, and customer data. Some POS systems require Adobe Air to function properly, which can be downloaded from this website. Ensuring you have the right software components in place allows you to leverage the full potential of your POS dashboard and make informed decisions for your business.
