RMM network monitoring is the unsung hero of modern network management, quietly safeguarding your systems and ensuring seamless operations. Imagine a network that proactively identifies and resolves issues before they impact your users, a network that alerts you to security threats in real-time, and a network that offers detailed insights into performance trends. This is the promise of RMM network monitoring, a powerful solution that empowers businesses to maintain a robust and resilient network infrastructure.
Table of Contents
This guide delves into the world of RMM network monitoring, exploring its core features, implementation strategies, and best practices. We’ll uncover how RMM tools can revolutionize your approach to network management, offering enhanced security, improved performance, and valuable insights to optimize your network for peak efficiency.
Introduction to RMM and Network Monitoring
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) and network monitoring are essential tools for managing and securing modern IT infrastructure. RMM provides a centralized platform for managing and monitoring endpoints, while network monitoring focuses on the health and performance of the network itself. Integrating these two technologies offers significant benefits for organizations of all sizes.
Defining RMM and Network Monitoring
RMM is a software solution that allows IT professionals to remotely monitor and manage devices across a network. This includes tasks such as software deployment, patch management, security updates, and troubleshooting. Network monitoring, on the other hand, involves tracking and analyzing network traffic, performance metrics, and security events to ensure optimal network functionality and identify potential issues.
The Importance of RMM for Network Security and Management
RMM plays a crucial role in enhancing network security and management by providing a comprehensive view of the IT environment. It enables proactive security measures, such as vulnerability scanning, endpoint security, and real-time threat detection. By automating routine tasks, RMM frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
Benefits of Integrating RMM with Network Monitoring, Rmm network monitoring
Integrating RMM with network monitoring offers a holistic approach to IT management, providing a unified view of both endpoints and the network infrastructure. This integration delivers several benefits:
- Enhanced Security: By combining endpoint and network monitoring, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of potential threats and vulnerabilities, enabling more effective security measures.
- Improved Performance: Integrated monitoring allows for real-time performance analysis of both endpoints and the network, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing resource utilization.
- Simplified Management: A single platform for managing both endpoints and the network streamlines IT operations, reducing complexity and improving efficiency.
- Proactive Problem Resolution: Integrated monitoring enables early detection of issues, allowing for proactive troubleshooting and minimizing downtime.
- Cost Savings: Automation of tasks and improved efficiency through integration lead to cost savings by reducing manual effort and minimizing downtime.
Implementing RMM Network Monitoring
Implementing an RMM network monitoring solution can significantly enhance your organization’s IT infrastructure security and performance. By proactively identifying and resolving potential issues, you can minimize downtime, improve user experience, and optimize resource utilization.
Network Infrastructure Planning
Effective network infrastructure planning is crucial for successful RMM implementation. This involves a comprehensive assessment of your current network, identifying potential bottlenecks and areas for improvement. It also includes defining your monitoring objectives, choosing the appropriate RMM tools, and designing a scalable and resilient network architecture.
- Network Topology Mapping: Create a detailed map of your network infrastructure, including all devices, connections, and protocols. This provides a visual representation of your network, allowing for easier identification of potential issues and optimization opportunities.
- Bandwidth Capacity Planning: Analyze your current bandwidth usage and forecast future requirements. This helps ensure that your network has sufficient capacity to handle current and future demands.
- Security Considerations: Implement appropriate security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, to protect your network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Configuring and Deploying Monitoring Tools
Once your network infrastructure is well-planned, you can begin configuring and deploying your RMM monitoring tools. This process involves selecting the right tools based on your specific needs, customizing monitoring parameters, and integrating the tools with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Tool Selection: Choose RMM tools that align with your monitoring objectives, budget, and technical expertise. Consider factors such as features, scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
- Configuration and Deployment: Follow the vendor’s instructions for configuring and deploying the monitoring tools. This typically involves setting up monitoring agents on your network devices, configuring alert thresholds, and defining reporting parameters.
- Integration: Integrate the RMM tools with your existing IT infrastructure, such as ticketing systems, asset management databases, and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions. This enables centralized monitoring and incident management.
Monitoring Key Network Metrics
Network monitoring involves tracking and analyzing key network metrics to gain insights into network performance, security, and overall health. This information helps identify potential issues, optimize resource allocation, and proactively address security threats.
Understanding Key Network Metrics
Monitoring key network metrics provides valuable insights into network performance, security, and resource utilization. These metrics help identify potential bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement.
- Bandwidth Utilization: Measures the amount of network bandwidth being used. High utilization can indicate potential bottlenecks or network congestion. Low utilization might suggest underutilized resources.
- Latency: Represents the time it takes for data packets to travel from source to destination. High latency can impact application responsiveness and user experience.
- Packet Loss: Indicates the percentage of data packets that are lost during transmission. High packet loss can lead to data corruption and application errors.
- Jitter: Measures the variation in delay for data packets. High jitter can impact voice and video communication quality.
- CPU Utilization: Tracks the percentage of CPU resources being used by network devices. High CPU utilization can indicate resource constraints or potential performance issues.
- Memory Utilization: Monitors the amount of memory being used by network devices. High memory utilization can lead to performance degradation and instability.
- Disk Usage: Tracks the amount of disk space used by network devices. High disk usage can indicate potential storage limitations or the need for capacity expansion.
- Security Events: Logs security-related events, such as failed login attempts, intrusion attempts, and malware activity. These events provide valuable insights into potential security threats.
Interpreting and Analyzing Network Data
Analyzing network data helps identify trends, anomalies, and potential issues. Tools like network performance monitoring (NPM) software can visualize and analyze network data, providing insights into network performance and security.
- Trend Analysis: Identifying patterns and trends in network metrics over time can help predict potential issues and proactively address them. For example, a gradual increase in bandwidth utilization over time could indicate the need for network capacity expansion.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifying sudden spikes or drops in network metrics can indicate potential issues or security threats. For instance, a sudden increase in latency could indicate a network outage or a denial-of-service attack.
- Correlation Analysis: Examining relationships between different network metrics can provide valuable insights into network performance. For example, a correlation between high CPU utilization and increased latency could indicate a CPU bottleneck impacting network performance.
Network Traffic Analysis for Security
Network traffic analysis plays a crucial role in identifying security threats and malicious activity. By analyzing network traffic patterns, organizations can detect suspicious activity, identify potential vulnerabilities, and respond to security incidents proactively.
- Protocol Analysis: Analyzing network traffic at the protocol level helps identify unusual or suspicious activity. For example, a sudden increase in traffic using a specific protocol might indicate a denial-of-service attack or a data exfiltration attempt.
- Packet Inspection: Examining individual network packets can reveal malicious content or suspicious activity. For example, analyzing packet payloads can identify malware or data exfiltration attempts.
- Traffic Anomaly Detection: Identifying deviations from normal network traffic patterns can indicate potential security threats. For example, a sudden surge in traffic from an unusual source could indicate a distributed denial-of-service attack.
- Security Event Correlation: Analyzing security events in conjunction with network traffic data provides a comprehensive view of potential security threats. For example, correlating a failed login attempt with suspicious network traffic patterns can indicate a targeted attack.
Troubleshooting Network Issues with RMM
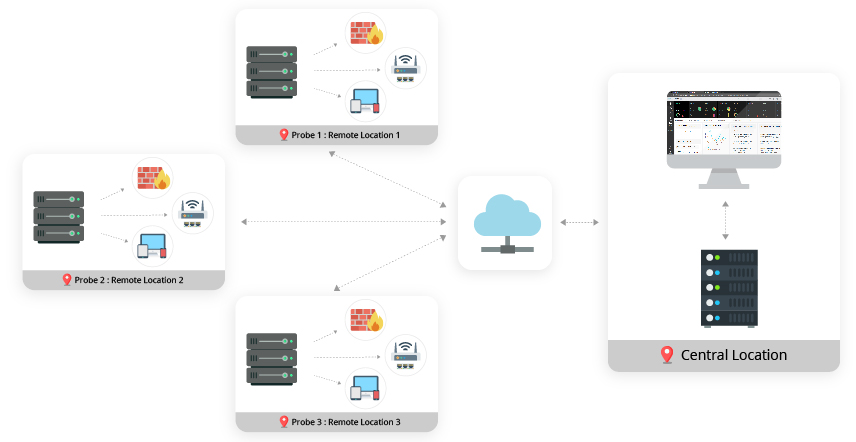
RMM tools can be incredibly valuable for troubleshooting network problems, offering a centralized platform for monitoring, diagnosing, and resolving issues. They provide real-time visibility into network performance, allowing you to identify bottlenecks, analyze traffic patterns, and pinpoint the root cause of problems.
Using RMM for Network Troubleshooting
RMM tools provide a comprehensive suite of features that simplify network troubleshooting. These include:
- Real-time Network Monitoring: RMM tools offer real-time dashboards that display key network metrics, such as bandwidth usage, latency, and packet loss. This allows you to quickly identify potential issues and monitor their impact on network performance.
- Remote Access and Control: RMM tools enable you to remotely access and control devices on your network, allowing you to diagnose problems and apply solutions without physically being present.
- Network Device Management: RMM tools streamline the management of network devices, including routers, switches, and firewalls. You can monitor their status, configure settings, and update firmware remotely.
- Log Analysis and Reporting: RMM tools collect and analyze network logs, providing insights into past events and helping you identify patterns that may indicate recurring problems.
Common Network Issues and Resolutions
RMM tools can be particularly helpful in resolving common network issues such as:
- Slow Network Performance: RMM tools can help you identify the source of slow network performance by analyzing bandwidth usage, latency, and packet loss. This can help you pinpoint congested network segments, faulty devices, or inefficient network configurations.
- Network Connectivity Issues: RMM tools can help you diagnose network connectivity problems by monitoring device connectivity status, analyzing network traffic patterns, and identifying potential network configuration errors.
- Security Threats: RMM tools can help you identify and respond to security threats by monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity, detecting malware infections, and implementing security policies.
Analyzing Network Logs and Performance Data
Network logs and performance data are crucial for troubleshooting network problems. RMM tools can help you analyze this data effectively:
- Log Analysis: RMM tools provide tools for analyzing network logs, allowing you to identify patterns, anomalies, and specific events that may have caused network issues. This can help you understand the timeline of events, identify the root cause of problems, and implement appropriate solutions.
- Performance Data Visualization: RMM tools often provide graphical representations of network performance data, making it easier to identify trends, anomalies, and potential issues. This can help you pinpoint network bottlenecks, identify devices with performance problems, and monitor the effectiveness of your troubleshooting efforts.
Security Considerations for RMM Network Monitoring
Integrating RMM with network monitoring can significantly enhance your IT operations, but it also introduces new security challenges. This section explores potential security risks and vulnerabilities associated with RMM network monitoring and provides recommendations for securing your RMM and network monitoring tools.
Security Risks and Vulnerabilities
It is essential to understand the potential security risks and vulnerabilities associated with RMM network monitoring. These risks can arise from various sources, including the RMM software itself, the network infrastructure, and user practices.
- RMM Software Vulnerabilities: RMM software, like any other software, can have vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your network and data. These vulnerabilities could allow attackers to steal sensitive information, install malware, or disrupt your network operations.
- Unauthorized Access: Unsecured RMM software or misconfigured access controls can allow unauthorized individuals to access your network monitoring data. This could lead to data breaches, privacy violations, and potential misuse of network information.
- Network Infrastructure Weaknesses: Weak network security practices, such as using default passwords, outdated software, or lack of firewalls, can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit to gain access to your RMM system and network.
- Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks can target users with malicious emails or websites designed to trick them into revealing their credentials or downloading malware. If successful, attackers could gain access to your RMM account and compromise your network.
Best Practices for RMM Network Monitoring
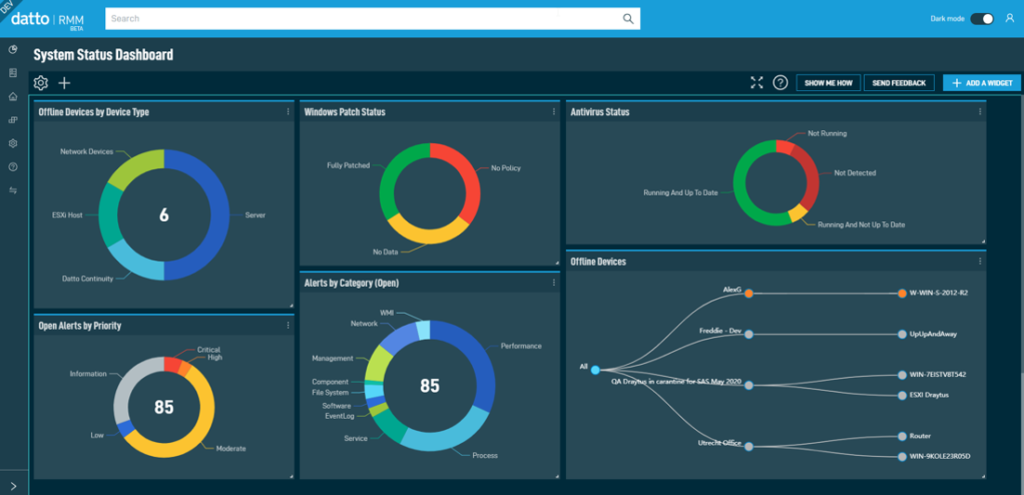
Optimizing RMM network monitoring for peak performance and efficiency is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of your IT infrastructure. This involves implementing best practices that go beyond simply setting up the monitoring system.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for proactive network management. Consistent monitoring allows you to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
- Schedule Regular Checks: Establish a routine for checking network performance and identifying any anomalies. This could involve daily, weekly, or monthly checks, depending on the criticality of your network.
- Perform Routine Maintenance: Regularly update your RMM software, network devices, and operating systems to ensure optimal performance and security. This includes patching vulnerabilities and applying security updates.
- Analyze Logs and Reports: Regularly review network logs and reports to gain insights into network behavior and identify potential issues. This allows you to address problems before they become significant.
Effective Alert Management
Effective alert management is crucial for responding to network issues promptly and efficiently. You need to configure alerts appropriately to minimize false positives and ensure that critical alerts are addressed promptly.
- Set Clear Alert Thresholds: Configure alert thresholds based on your network’s specific requirements and acceptable performance levels. This ensures that you receive alerts only for significant events, reducing alert fatigue.
- Establish Alert Escalation Procedures: Define a clear escalation process for alerts, ensuring that the appropriate team members are notified in a timely manner. This could involve escalating alerts to different levels of support based on severity.
- Use Different Alert Channels: Utilize various alert channels, such as email, SMS, or push notifications, to ensure that critical alerts reach the responsible personnel regardless of their location or device.
Future Trends in RMM Network Monitoring
The landscape of network management is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the increasing complexity of modern networks. As these technologies mature, RMM solutions are adapting to provide more comprehensive and intelligent network monitoring capabilities.
Impact of Cloud Computing
The adoption of cloud computing has significantly impacted network monitoring. Cloud-based RMM solutions offer several advantages, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. They enable organizations to monitor their networks from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. Cloud-based RMM solutions can also easily scale to accommodate growing network demands, ensuring that organizations have the resources they need to manage their networks effectively.
- Increased flexibility and scalability: Cloud-based RMM solutions can easily scale to accommodate growing network demands, ensuring organizations have the resources needed to manage their networks effectively.
- Improved accessibility: Cloud-based RMM solutions allow organizations to monitor their networks from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud-based RMM solutions often have lower upfront costs compared to traditional on-premises solutions, making them more accessible to organizations of all sizes.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
AI is playing an increasingly important role in network management, enabling RMM solutions to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that would be difficult for humans to detect. AI-powered RMM solutions can automate tasks such as anomaly detection, performance optimization, and security threat identification.
- Predictive maintenance: AI can analyze network data to identify potential issues before they occur, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Automated incident response: AI-powered RMM solutions can automatically detect and respond to security threats, minimizing the impact of attacks.
- Enhanced network performance: AI can optimize network configurations and resource allocation to improve performance and reduce latency.
Predictions for the Future of RMM Network Monitoring
The future of RMM network monitoring solutions is bright, with several exciting developments on the horizon.
- Increased automation: RMM solutions will become increasingly automated, leveraging AI and machine learning to streamline network management tasks.
- Integration with other IT tools: RMM solutions will integrate seamlessly with other IT tools, such as ticketing systems and asset management platforms, creating a unified view of the IT infrastructure.
- Enhanced security features: RMM solutions will incorporate advanced security features, such as threat intelligence and vulnerability scanning, to protect networks from evolving cyber threats.
Epilogue: Rmm Network Monitoring
As technology continues to evolve, the need for comprehensive and proactive network management becomes ever more critical. RMM network monitoring provides a powerful framework for achieving this goal, enabling businesses to safeguard their networks, optimize performance, and gain valuable insights into network behavior. By embracing RMM tools and adopting best practices, organizations can build a more resilient, secure, and efficient network infrastructure, ultimately supporting their business objectives and driving success.
RMM network monitoring provides a comprehensive view of your network’s health, alerting you to potential issues before they become major problems. But what if you need to manage audio routing and mixing for a conference call or online meeting?
That’s where Voicemeeter comes in, a powerful audio mixer that can streamline your audio setup. By combining RMM network monitoring with a tool like Voicemeeter, you can ensure both your network and your audio are running smoothly, making your online communications seamless.
