MS Word 2007, a cornerstone of productivity for many, ushered in a new era of word processing with its intuitive interface and powerful features. This guide delves into the heart of this software, exploring its functionalities, navigating its user interface, and showcasing its capabilities for document creation, formatting, and collaboration.
Table of Contents
From the basics of document creation to the intricacies of advanced features like mail merge and macros, we’ll unpack the tools that make MS Word 2007 a valuable asset for students, professionals, and anyone seeking to create and manage high-quality documents.
User Interface and Navigation
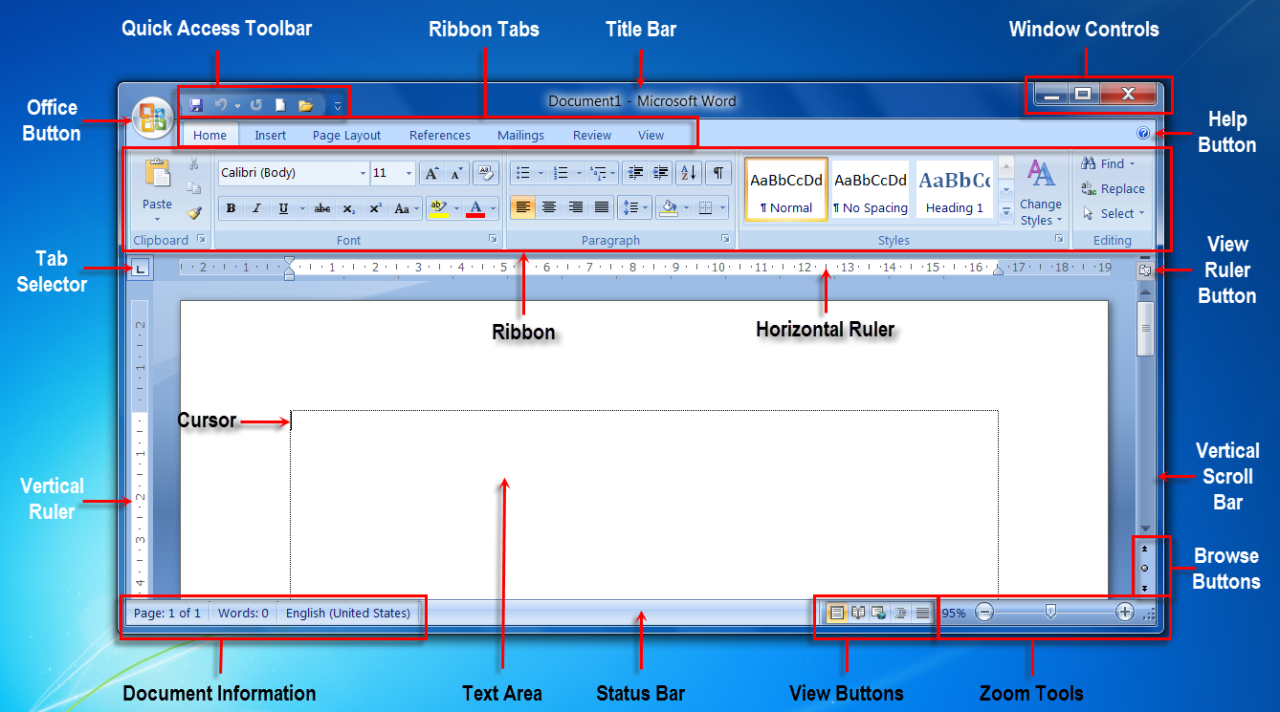
Microsoft Word 2007 introduced a significant overhaul of its user interface, aiming to enhance user experience and accessibility. The new interface features a Ribbon, Quick Access Toolbar, and other elements designed for efficient document creation and editing.
The Ribbon
The Ribbon is a central element of the Word 2007 interface, replacing the traditional menus and toolbars. It is a horizontal bar located at the top of the application window, divided into tabs. Each tab represents a specific category of features, such as Home, Insert, Page Layout, References, Mailings, Review, and View.
Within each tab, groups of related commands are organized into smaller sections, allowing users to easily find the tools they need. For instance, the Home tab includes groups for Clipboard, Font, Paragraph, and Editing.
The Ribbon offers a streamlined approach to accessing commands, making it easier for users to navigate and find the tools they need. It also provides context-sensitive functionality, displaying relevant commands based on the active document element or task.
Quick Access Toolbar
The Quick Access Toolbar is located above the Ribbon, providing quick access to frequently used commands. By default, it includes tools like Save, Undo, and Redo. Users can customize the toolbar to include their preferred commands, enhancing productivity by providing immediate access to essential tools.
Navigation Methods
Word 2007 offers various navigation methods to efficiently move through documents and access different features.
Menus and Toolbars
While the Ribbon replaces the traditional menus, it still retains some menu-based functionality. Clicking the File tab opens the Backstage view, providing access to document-related options like saving, printing, and sharing. Additionally, some tools within the Ribbon may have drop-down menus or sub-menus for further options.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Word 2007 supports numerous keyboard shortcuts, allowing users to perform actions quickly without using the mouse. These shortcuts can be accessed by pressing a combination of keys, such as Ctrl+C for copy, Ctrl+V for paste, and Ctrl+S for save.
Mouse Interactions
Users can interact with the interface using the mouse to select text, navigate through documents, and access commands. Clicking on different elements of the interface, such as buttons, tabs, or icons, triggers specific actions.
Other Elements
Besides the Ribbon and Quick Access Toolbar, Word 2007 includes other elements that contribute to the user interface:
| Element | Function |
|---|---|
| Status Bar | Displays information about the document, such as page number, word count, and language. |
| View Buttons | Provides different document views, including Print Layout, Web Layout, and Artikel. |
| Zoom Slider | Adjusts the document’s magnification level. |
Document Creation and Formatting
Creating and formatting documents in MS Word 2007 is a fundamental skill for anyone who needs to produce professional-looking documents. This section will guide you through the process of creating a new document, understanding file types and templates, and exploring the various formatting options available.
Creating a New Document
To create a new document in MS Word 2007, you can use the following steps:
- Click on the “Microsoft Office Button” located in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Select “New” from the menu.
- Choose a template or select “Blank document” to start from scratch.
- Click “Create” to open the new document.
MS Word 2007 offers various file types for saving your documents, including:
- .docx: The default file format for MS Word 2007 and later versions. It’s a compressed XML-based format that allows for rich formatting and compatibility with other applications.
- .doc: The older file format used by earlier versions of MS Word. While it’s still supported, it’s recommended to use the .docx format for better compatibility and features.
- .rtf: Rich Text Format is a cross-platform file format that can be opened and edited in various word processing applications.
- .pdf: Portable Document Format is a widely used format for sharing and viewing documents. MS Word 2007 allows you to save your documents as PDFs.
Templates provide pre-designed document structures and layouts for various purposes, such as letters, resumes, reports, and brochures. They can save you time and effort by providing a starting point for your document.
Formatting Options
MS Word 2007 offers a wide range of formatting options to enhance the visual appeal and readability of your documents. These options include:
Fonts
Fonts play a crucial role in defining the appearance of your text. MS Word 2007 offers a vast library of fonts, allowing you to choose the best font for your document’s purpose and style.
- Font Style: Choose from regular, bold, italic, or bold italic styles to emphasize specific text.
- Font Size: Adjust the size of your text to enhance readability and create visual hierarchy.
- Font Color: Use different colors to highlight key information or create visual interest.
Paragraph Styles
Paragraph styles define the overall appearance of your paragraphs, including indentation, spacing, alignment, and line spacing.
- Alignment: Choose from left, right, center, or justified alignment to control the positioning of text within the paragraph.
- Indentation: Indent the first line of your paragraphs to improve readability and visual flow.
- Spacing: Adjust the spacing between lines and paragraphs to create visual balance and enhance readability.
Page Layout
Page layout refers to the overall arrangement of elements on your document page. MS Word 2007 provides options for customizing the margins, page orientation, and header and footer content.
- Margins: Define the space around the edges of your document to create a balanced layout.
- Orientation: Choose between portrait (vertical) or landscape (horizontal) orientation to fit your content.
- Headers and Footers: Add page numbers, document titles, or other information to the top and bottom of each page.
Applying Formatting Techniques, Ms word 2007
Here’s a step-by-step guide on applying basic and advanced formatting techniques in MS Word 2007:
Basic Formatting
- Selecting Text: To apply formatting to text, you must first select it. Use your mouse to drag over the desired text or use the keyboard shortcuts (Ctrl + A for selecting all text, Shift + arrow keys for selecting word by word, etc.).
- Using the Formatting Toolbar: The formatting toolbar provides quick access to common formatting options. Click on the “Home” tab to access the formatting toolbar. Use the buttons for font style, font size, font color, alignment, indentation, and line spacing.
- Using the Formatting Dialog Box: For more advanced formatting options, click on the “Font” or “Paragraph” button in the formatting toolbar to access the respective dialog boxes. These dialog boxes offer a wider range of customization options.
Advanced Formatting
- Using Styles: Styles are pre-defined sets of formatting attributes that can be applied to text, paragraphs, or entire documents. You can create your own styles or use the built-in styles. To apply a style, select the text and click on the desired style from the “Styles” gallery in the “Home” tab.
- Using Tabs: Tabs are used to align text in specific columns. You can create and customize tab stops to create a structured layout for your document. Click on the “Page Layout” tab and then click on the “Paragraph” group. Click on the “Tabs” button to access the “Tabs” dialog box.
- Using Borders and Shading: Borders and shading can be used to visually separate sections of your document or highlight important information. Select the text or object you want to format, click on the “Home” tab, and then click on the “Borders” or “Shading” button in the “Paragraph” group.
Advanced Features and Functionality
MS Word 2007 offers a range of advanced features that can significantly enhance document creation and productivity. These features provide users with powerful tools for automating tasks, customizing documents, and protecting sensitive information.
Mail Merge
Mail merge is a powerful feature that allows users to create personalized documents by combining a main document with a data source. This feature is particularly useful for creating mass mailings, such as newsletters, invitations, or marketing materials.
The main document contains the basic template of the document, including text, images, and placeholders for the data. The data source, usually a spreadsheet or database, provides the information that will be merged into the main document. This allows for creating personalized documents that are tailored to each recipient.
For example, a business might use mail merge to create personalized letters to potential customers, including their names and addresses. Or, a teacher could use mail merge to create personalized certificates for each student, including their names and scores.
The benefits of using mail merge include:
- Saving time and effort by automating the process of creating multiple documents.
- Ensuring consistency and accuracy in the content of multiple documents.
- Creating personalized documents that are tailored to each recipient.
However, mail merge can be complex to set up and requires a basic understanding of data sources and placeholders.
Macros
Macros are sequences of commands or actions that can be recorded and then played back to automate repetitive tasks. This feature can significantly improve productivity by eliminating the need to manually perform these tasks.
For example, a user could record a macro to format a document, insert a table, or create a new page. Once the macro is recorded, it can be played back at any time to perform the same actions quickly and efficiently.
Macros can be used to automate a wide range of tasks, including:
- Formatting documents, such as applying styles, adding headers and footers, and inserting tables.
- Inserting and manipulating objects, such as images, charts, and tables.
- Creating and editing documents, such as inserting new pages, deleting content, and saving files.
However, macros can be complex to create and debug, and they may not be compatible with all versions of MS Word.
Document Protection
Document protection features allow users to control access to their documents and prevent unauthorized modifications. This feature is essential for protecting sensitive information, such as financial reports, legal documents, or confidential communications.
MS Word 2007 offers several document protection features, including:
- Password Protection: Users can set passwords to restrict access to documents, preventing unauthorized individuals from opening or editing them.
- Read-Only Mode: Users can set documents to read-only mode, allowing others to view the document but not make any changes.
- Restrict Editing: Users can restrict editing to specific parts of a document, preventing others from modifying certain sections.
These features help ensure the integrity and confidentiality of documents, but they may not be effective against all types of security threats.
Conclusion (Avoid this section): Ms Word 2007
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of Microsoft Word 2007, exploring its user interface, document creation and formatting capabilities, and advanced features. The article emphasized the key features of Word 2007, including its intuitive ribbon interface, enhanced document formatting options, and powerful collaboration tools.
Understanding the Significance of MS Word 2007
MS Word 2007 marked a significant evolution in the world of word processing, introducing a user-friendly interface and powerful features that have become staples in modern word processing applications. Its intuitive design, enhanced formatting capabilities, and robust collaboration tools made it a popular choice for both individual users and businesses.
Final Conclusion
Whether you’re a seasoned user or a newcomer to MS Word 2007, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to confidently navigate its features and unlock its full potential. From the initial steps of document creation to the intricacies of advanced functionalities, MS Word 2007 empowers you to communicate effectively, streamline your workflow, and achieve your document-related goals.
While Microsoft Word 2007 is great for text editing and formatting, you might need a different tool for audio editing. If you’re looking for a free and powerful audio editor, consider downloading Audacity here. Audacity can be a valuable addition to your workflow, especially if you need to edit audio files for your Word documents or other projects.
