3D Studio Max, often referred to as 3ds Max, is a powerful 3D modeling, animation, and rendering software that has become a staple in the world of visual effects, game development, and architectural visualization. Developed by Autodesk, 3ds Max has a rich history, evolving over decades to meet the ever-changing demands of the industry. From its humble beginnings as a DOS-based program, 3ds Max has become a sophisticated and versatile tool, offering a wide range of features and functionalities for creating stunning 3D content.
Table of Contents
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious beginner, 3ds Max offers a wealth of possibilities for bringing your creative visions to life. With its intuitive interface, robust modeling tools, and advanced animation features, 3ds Max empowers users to create everything from intricate characters and environments to photorealistic renderings and captivating animations. Its versatility extends across various industries, including film and television, video games, architecture, product design, and more.
Interface and Workflow
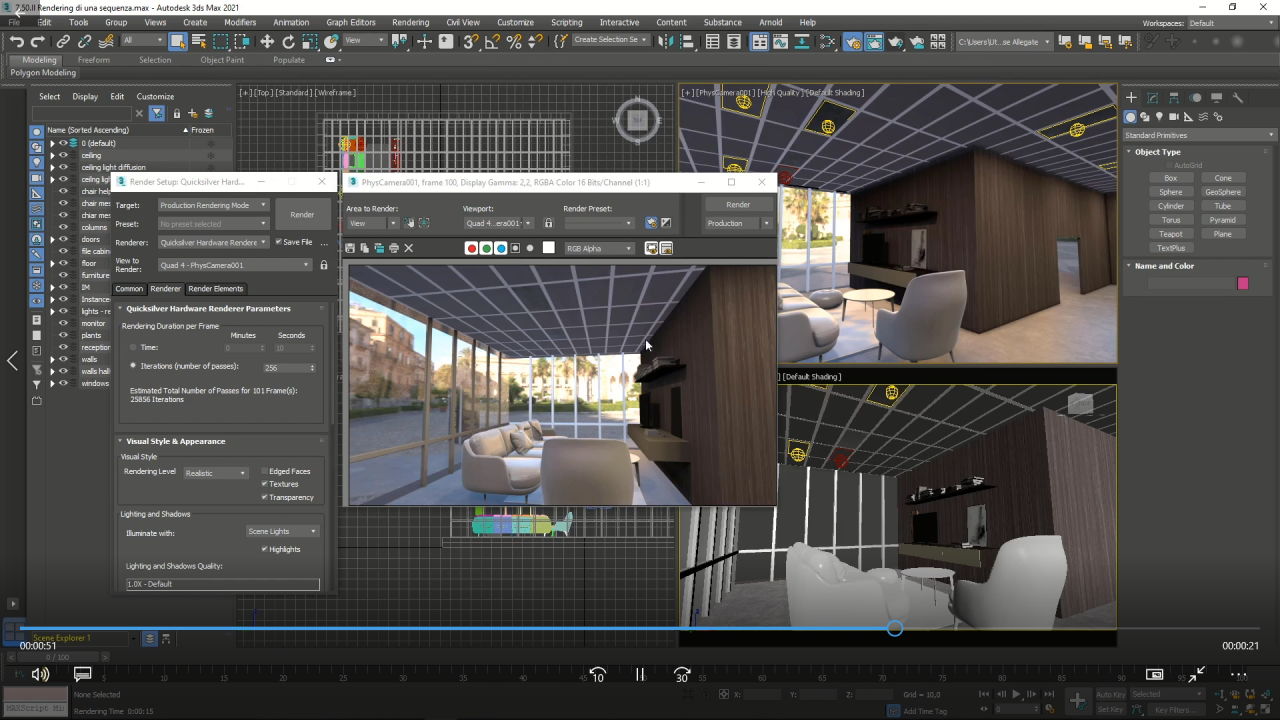
3ds Max offers a comprehensive and intuitive interface, designed to streamline the process of creating stunning 3D models, animations, and scenes. The software provides a wide range of tools and features catering to both beginners and experienced professionals. This section will explore the layout of the 3ds Max interface, delve into common tools, and Artikel the workflow process for creating 3D content.
Interface Layout
The 3ds Max interface is organized into several key components, each serving a specific purpose.
- Main Menu Bar: Located at the top of the screen, this bar provides access to various menus and commands, such as File, Edit, View, and Tools. These menus offer options for managing files, modifying objects, customizing the interface, and accessing various tools.
- Toolbars: Positioned below the Main Menu Bar, toolbars provide quick access to frequently used tools and commands. Customizable toolbars allow users to arrange and group tools according to their preferences.
- Viewport: This is the central area where the 3D scene is displayed. Users can interact with objects, manipulate cameras, and visualize the scene from different angles.
- Command Panel: Located on the right side of the screen, the Command Panel provides access to various options and settings for selected objects, modifiers, and other elements within the scene. This panel offers a comprehensive range of controls for manipulating objects, applying materials, and customizing scene settings.
- Status Bar: At the bottom of the screen, the Status Bar displays information about the current state of the software, including mouse coordinates, selected objects, and system performance.
Common Tools
3ds Max provides a wide array of tools for modeling, animation, rendering, and more. Some of the most common tools include:
- Modeling Tools: These tools enable users to create and manipulate 3D objects. Common modeling tools include:
- Box: Creates a rectangular prism.
- Sphere: Creates a sphere.
- Cylinder: Creates a cylinder.
- Extrude: Creates a 3D object by extruding a 2D shape along a path.
- Loft: Creates a 3D object by lofting a series of curves.
- Patch: Creates a 3D object by manipulating a network of control points.
- Animation Tools: These tools enable users to create and control animation. Common animation tools include:
- Keyframing: Allows users to set keyframes at specific times to define the object’s position, rotation, and scale.
- Motion Paths: Enables users to create paths for objects to follow during animation.
- Character Animation: Provides tools for animating characters, including bones, skinning, and facial expressions.
- Rendering Tools: These tools enable users to create high-quality images and videos of the 3D scene. Common rendering tools include:
- Mental Ray: A powerful rendering engine that produces photorealistic images.
- V-Ray: Another popular rendering engine known for its advanced features and realistic rendering capabilities.
- Corona Renderer: A fast and efficient rendering engine designed for both beginners and professionals.
Workflow Process
The workflow process for creating 3D content in 3ds Max typically involves several stages:
- Modeling: This stage involves creating the 3D objects that will be used in the scene. Users can utilize various modeling tools to create objects from scratch or import existing models.
- Texturing: After modeling, objects are typically textured to add visual detail and realism. Textures can be created using various software programs or imported from external sources.
- Lighting: Lighting is crucial for creating a visually appealing scene. 3ds Max provides tools for adding lights to the scene and adjusting their properties, such as color, intensity, and shadows.
- Animation: This stage involves animating objects and characters within the scene. Users can use keyframing, motion paths, and other animation tools to create dynamic and engaging animations.
- Rendering: The final stage involves rendering the scene to create a high-quality image or video. Users can choose from various rendering engines and settings to achieve the desired visual quality.
Navigating the 3ds Max Interface
For beginners, navigating the 3ds Max interface can be overwhelming at first. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Familiarize yourself with the main interface components: Start by understanding the purpose of the Main Menu Bar, Toolbars, Viewport, Command Panel, and Status Bar.
- Explore the basic modeling tools: Begin by experimenting with simple modeling tools like Box, Sphere, and Cylinder. Learn how to create and manipulate these basic shapes.
- Create a simple scene: Use the modeling tools to create a few basic objects and arrange them in the Viewport.
- Learn about materials and textures: Explore the materials and textures available in 3ds Max. Apply different materials to your objects to see how they affect their appearance.
- Experiment with lighting: Add lights to your scene and adjust their properties to see how they influence the overall lighting and shadows.
- Try basic animation: Learn how to use keyframing to create simple animations for your objects.
- Explore the rendering options: Experiment with different rendering engines and settings to see how they affect the final output.
Modeling Techniques
Modeling is the process of creating 3D objects in 3ds Max. It involves shaping and manipulating vertices, edges, and faces to form the desired geometry. There are various techniques available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. This section will explore the most common techniques, their applications, and their tools in 3ds Max.
Polygon Modeling
Polygon modeling is the most fundamental and widely used technique in 3ds Max. It involves creating and manipulating polygons, which are the basic building blocks of 3D models. Polygons are flat, two-dimensional shapes that define the surface of an object.
Polygon modeling offers a high degree of control over the shape and detail of a model. It is well-suited for creating organic shapes, complex geometries, and detailed models. The main tools used in polygon modeling include:
- Vertex, Edge, and Face Selection: These tools allow you to select and manipulate individual vertices, edges, and faces.
- Extrude: This tool creates new geometry by pushing a selected face or edge along a normal direction.
- Bevel: This tool rounds off sharp edges and corners, creating smooth transitions.
- Chamfer: This tool creates a flat edge by cutting off a portion of the original edge.
- Inset: This tool creates a new face inside a selected face, allowing you to add detail or create a hollow shape.
- Bridge: This tool creates a smooth transition between two selected edges or faces.
- Weld: This tool merges selected vertices into a single vertex.
- Delete: This tool removes selected vertices, edges, or faces.
Polygon modeling is a versatile technique that allows for a wide range of creative possibilities. However, it can be time-consuming and require a high level of skill to achieve complex and detailed models.
NURBS Modeling
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) modeling is another powerful technique used in 3ds Max. NURBS surfaces are mathematically defined and offer smooth, continuous curves and surfaces. They are ideal for creating organic shapes, such as cars, airplanes, and characters.
NURBS modeling offers a high degree of control over the curvature and smoothness of a model. It is also less prone to polygon count issues, which can affect rendering performance. The main tools used in NURBS modeling include:
- CV (Control Vertex) Manipulation: CVs are points that define the shape of a NURBS surface. By manipulating these points, you can change the curve or surface.
- Degree: The degree of a NURBS curve or surface determines its smoothness. Higher degrees result in smoother curves.
- Knots: Knots are points along a NURBS curve or surface that control the distribution of CVs.
- Trim: This tool allows you to cut and trim NURBS surfaces, creating complex shapes.
- Extend: This tool allows you to extend a NURBS curve or surface.
NURBS modeling is often used for creating high-quality, smooth models. It requires a deeper understanding of mathematical principles, but it offers greater control over the shape and curvature of a model.
Procedural Modeling
Procedural modeling is a technique that uses algorithms and rules to generate geometry automatically. This allows for creating complex and intricate models with minimal user input.
Procedural modeling is often used for creating repetitive patterns, organic shapes, and complex structures. It is also used for creating variations of a model, such as different sizes or shapes. Some common tools used in procedural modeling include:
- Array: This tool creates multiple copies of an object, arranged in a specific pattern.
- Spline IK (Inverse Kinematics): This tool allows you to control the position of an object’s end point, while the rest of the object automatically adjusts its shape.
- Geometry Generator: This tool allows you to create geometry based on mathematical formulas or procedural rules.
- Noise: This tool adds randomness and irregularity to geometry, creating organic shapes and textures.
- Fractals: This tool generates complex and self-similar patterns, often used for creating natural structures.
Procedural modeling is a powerful technique for creating complex models with minimal effort. It is often used in conjunction with other modeling techniques, such as polygon modeling or NURBS modeling.
Modeling a 3D Character
This example will demonstrate the use of polygon modeling to create a simple 3D character.
1. Create a Sphere: Begin by creating a sphere using the Create menu.
2. Edit the Sphere: Select the sphere and use the Edit Poly modifier to edit its geometry.
3. Extrude the Sphere: Use the Extrude tool to create a head, arms, and legs.
4. Bevel the Edges: Use the Bevel tool to round off the sharp edges of the character’s limbs.
5. Add Detail: Use the Inset and Extrude tools to add detail to the character’s face, hands, and feet.
6. Add Eyes and Mouth: Create small spheres for the eyes and use the Extrude tool to create a mouth.
7. Add a Material: Apply a material to the character to give it a more realistic appearance.
This is a simple example, but it demonstrates the basic principles of polygon modeling. By using the tools and techniques described above, you can create a wide variety of 3D characters.
Materials and Texturing
Materials and textures are crucial elements in 3ds Max, as they add realism and visual appeal to your 3D models. They define the appearance of surfaces, adding depth, color, and visual interest to your creations. This section will delve into the different types of materials and textures available in 3ds Max, explaining the process of applying them to your models and demonstrating how to create custom materials and textures.
Types of Materials and Textures
Materials in 3ds Max are the foundation for defining the appearance of your 3D objects. They determine how light interacts with the surface, influencing the object’s color, reflectivity, and overall visual characteristics. 3ds Max offers a wide range of material types, each with unique properties.
- Standard Material: This is the basic material type in 3ds Max, providing fundamental properties like color, diffuse, specular, and ambient. It is a good starting point for simple materials.
- Blinn Material: This material type offers a more refined specular highlight than the Standard Material, providing a smoother and more realistic appearance. It is particularly useful for materials like metals and plastics.
- Phong Material: This material type uses a Phong shading model, known for its sharp specular highlights, creating a more dramatic and glossy effect. It is ideal for materials like polished metals and glass.
- Arch & Design Material: This material type is specifically designed for architectural and design applications, providing a wide range of options for simulating materials like wood, stone, and concrete.
- Multi/Sub-Object Material: This material type allows you to apply different materials to different parts of your object, giving you greater control over its appearance.
Textures are images or patterns that can be applied to materials to add detail and realism. They can be used to simulate a variety of surfaces, such as wood grain, fabric, or stone. 3ds Max supports various texture types:
- Bitmap Texture: This is the most common type of texture, using an image file as the source for the texture. You can use various image formats like JPG, PNG, and TIFF.
- Procedural Texture: This type of texture is generated mathematically, providing endless possibilities for creating unique patterns and effects. Examples include noise textures, marble textures, and wood textures.
- Composite Texture: This type of texture combines different textures to create complex and realistic effects. You can combine bitmap textures, procedural textures, or even other composite textures.
- Environment Texture: This type of texture is used to create reflections and refractions in your scene. It is typically used for the background or environment of your scene.
Applying Materials and Textures
Applying materials and textures to your 3D models is a straightforward process in 3ds Max. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Select the object: In the viewport, select the object to which you want to apply the material.
2. Open the Material Editor: Go to the “Materials” tab in the main toolbar and click the “Material Editor” button.
3. Create a new material: In the Material Editor, click the “Create” button and select the desired material type from the dropdown menu.
4. Apply the material: In the viewport, select the object again and click the “Assign Material to Selection” button in the Material Editor.
5. Apply the texture: In the Material Editor, click the “Diffuse” map slot (or any other map slot depending on the material type).
6. Select the texture: Click the “Bitmap” button and navigate to the desired texture file.
7. Adjust texture parameters: In the Material Editor, you can adjust the texture parameters like scale, offset, and rotation to fine-tune the texture’s appearance on the object.
Creating Custom Materials and Textures
Creating custom materials and textures in 3ds Max allows you to achieve unique and realistic visual effects. Here’s how you can design a custom material and texture for a 3D object:
1. Choose a base material: Start by selecting a suitable base material type from the Material Editor, such as the Standard Material or the Blinn Material.
2. Adjust material properties: Modify the material properties to match the desired appearance. For example, you can adjust the color, diffuse, specular, and ambient values.
3. Create a custom texture: You can create a custom texture using various methods, such as:
– Bitmap Texture: Create an image in a suitable image editing software like Photoshop or GIMP and import it into 3ds Max as a bitmap texture.
– Procedural Texture: Use the various procedural texture generators in 3ds Max to create unique patterns and effects.
– Composite Texture: Combine different textures using the Composite Map in the Material Editor.
4. Apply the texture: Assign the custom texture to the desired map slot in the Material Editor, such as the Diffuse map slot.
5. Adjust texture parameters: Fine-tune the texture’s appearance on the object by adjusting the texture parameters like scale, offset, and rotation.
Example: To create a custom material and texture for a wooden table, you could start with the Arch & Design Material and adjust the color and grain properties to resemble wood. Then, you could create a procedural wood texture using the “Wood” generator in the Material Editor. You can adjust the parameters of the wood texture to create different variations in grain and color. Finally, apply the texture to the Diffuse map slot of the Arch & Design Material.
Plugins and Extensions
Plugins and extensions are essential tools that expand the capabilities of 3ds Max, offering a wide range of functionalities and features that go beyond the software’s built-in tools. They allow users to streamline workflows, enhance modeling, animation, rendering, and post-production processes, and access specialized tools for specific tasks.
Popular Plugins and Extensions, 3d studio max
The 3ds Max plugin ecosystem is vast and diverse, offering solutions for various needs. Here are some popular plugins and extensions:
- V-Ray: A renowned rendering engine known for its photorealistic rendering capabilities, offering advanced features like global illumination, physically based materials, and high-quality output.
- Corona Renderer: Another powerful rendering engine with a user-friendly interface and fast render times. It features physically based materials, realistic lighting, and efficient rendering workflows.
- Octane Render: A GPU-accelerated rendering engine that excels in speed and efficiency, particularly for complex scenes and real-time visualization. It offers physically based materials, advanced lighting, and high-resolution rendering.
- Chaos Group Phoenix FD: A fluid dynamics simulation plugin that enables realistic fluid simulations for water, smoke, fire, and other effects. It provides tools for controlling fluid behavior, creating realistic effects, and integrating them into 3ds Max scenes.
- FumeFX: A popular fluid simulation plugin that offers advanced features for creating realistic smoke, fire, and other fluid effects. It provides tools for controlling fluid behavior, creating complex simulations, and integrating them into 3ds Max scenes.
- X-Particles: A powerful particle system plugin that allows users to create complex particle effects, simulations, and animations. It offers a wide range of tools for controlling particle behavior, creating realistic effects, and integrating them into 3ds Max scenes.
- Forest Pack: A plugin that simplifies the creation and management of large-scale environments, such as forests, fields, and urban landscapes. It allows users to create realistic vegetation, distribute objects efficiently, and manage large-scale scenes.
- RailClone: A plugin that facilitates the creation and management of complex repeating objects, such as railings, fences, and other linear structures. It provides tools for creating parametric objects, defining their geometry, and generating complex arrangements.
- MeshTools: A plugin that expands the modeling capabilities of 3ds Max, offering tools for creating complex geometry, manipulating meshes, and creating detailed models. It provides a range of tools for smoothing, subdividing, and manipulating meshes.
- Quixel Megascans: A library of high-quality 3D assets, including textures, materials, and models, that can be integrated into 3ds Max scenes. It offers a wide range of assets for various environments and objects, providing realistic and detailed visual content.
Benefits of Using Plugins
Plugins offer several benefits, including:
- Enhanced Functionality: Plugins expand the capabilities of 3ds Max, providing tools and features not available in the base software.
- Workflow Optimization: Plugins can streamline workflows, automate tasks, and improve efficiency.
- Specialized Tools: Plugins provide specialized tools for specific tasks, such as rendering, animation, modeling, and simulation.
- Access to Advanced Features: Plugins often offer advanced features and functionalities that are not available in the base software.
- Community Support: Many plugins have active communities, providing support, tutorials, and resources.
Installing and Using a Plugin
Installing and using plugins in 3ds Max is generally straightforward. The process typically involves downloading the plugin from the developer’s website, extracting the files, and placing them in the appropriate 3ds Max directory. Once installed, the plugin can be accessed through the 3ds Max interface, usually through a new menu or toolbar.
Example: To install the V-Ray plugin, you would download the installer from Chaos Group’s website, run the installer, and follow the on-screen instructions. Once installed, V-Ray’s options and tools would be accessible through a new menu or toolbar in 3ds Max.
Best Practices and Optimization
Creating efficient and optimized 3D models and scenes in 3ds Max is crucial for smooth workflow, faster rendering times, and smaller file sizes. This section explores best practices and techniques to achieve these goals, enabling you to create high-quality 3D content with optimal performance.
Model Optimization
Optimizing your models is a fundamental step in achieving efficient rendering and smaller file sizes. Efficiently designed models reduce the workload on your computer, resulting in faster rendering times and improved performance.
- Reduce Polygons: High-polygon models can significantly impact rendering performance. Use modeling techniques like decimation, optimization, and simplification to reduce the polygon count while maintaining the visual quality of your models. Tools like the “MeshSmooth” modifier can be used to create smooth surfaces with fewer polygons.
- Optimize Geometry: Avoid unnecessary geometry, such as overlapping faces or edges. Clean up your models using tools like “Weld” and “Remove Duplicate Faces” to streamline the geometry and reduce the overall complexity.
- Use Proper Topology: Employ clean and organized topology, avoiding unnecessary edges or loops. This improves the overall quality and reduces the number of polygons needed to represent the model.
- Simplify Textures: High-resolution textures can consume a significant amount of memory and slow down rendering. Optimize textures by reducing their resolution or using compression techniques. Use tools like Photoshop or other image editing software to compress and optimize textures for web and game development.
Scene Optimization
Optimizing your scene involves techniques that reduce the overall complexity and enhance rendering efficiency.
- Use Proper Units: Set the correct units for your scene to avoid scaling issues and maintain accurate proportions. Using consistent units helps to prevent errors and ensures that your scene is rendered correctly.
- Minimize Objects: Reduce the number of objects in your scene by combining or grouping similar objects. This reduces the workload on the renderer and improves performance. For example, if you have multiple identical chairs, you can group them together to treat them as a single object.
- Use Layers: Organize your scene by using layers to separate different elements. This allows you to easily hide or isolate specific objects during the rendering process, improving performance and workflow.
- Optimize Materials: Simplify materials by using fewer textures and reducing the number of maps. This reduces the amount of data the renderer needs to process, leading to faster rendering times.
- Use Proxy Objects: For large and complex models, use proxy objects to represent them in your scene. Proxy objects are lightweight placeholders that reduce the rendering load without affecting the final result. You can then replace them with the full-resolution model for final rendering.
Rendering Optimization
Rendering optimization involves techniques that improve the efficiency of the rendering process, leading to faster render times and improved performance.
- Use Render Settings: Optimize your render settings to balance quality and performance. Experiment with different render settings, such as sampling rates, anti-aliasing, and render passes, to find the optimal balance for your project.
- Use Render Elements: Break down your rendering into separate elements, such as color, depth, and normal maps. This allows you to composite the final image later, providing more control and flexibility. You can then use the individual elements to create different effects or variations of your image.
- Use Render Farms: For large and complex scenes, consider using render farms. Render farms distribute the rendering workload across multiple computers, significantly reducing the overall rendering time.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting common issues in 3ds Max involves understanding the underlying causes and applying appropriate solutions.
- Render Errors: Analyze the error messages and identify the specific cause of the problem. Common issues include missing textures, incorrect material settings, or memory limitations. Check your scene for any inconsistencies or missing files.
- Slow Rendering: Identify the bottlenecks in your scene that are causing slow rendering times. This may involve analyzing the complexity of your models, the number of objects, or the size of your textures. Optimize your scene and render settings to improve performance.
- Model Issues: Check your models for any errors, such as overlapping faces, flipped normals, or missing vertices. Use tools like “MeshSmooth” or “Weld” to resolve these issues and ensure a clean and optimized model.
Resources and Learning Materials
Learning 3ds Max can be a rewarding journey, but it’s important to have access to the right resources and learning materials. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned professional, there are countless avenues to expand your skills and stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and advancements.
Online Resources and Tutorials
The internet is a treasure trove of 3ds Max resources, offering a vast array of tutorials, articles, and communities to support your learning.
- Autodesk Knowledge Network (AKN): This official resource from Autodesk provides comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and support articles covering various aspects of 3ds Max. You can find detailed explanations of features, workflows, and troubleshooting tips.
- YouTube: Platforms like YouTube offer a plethora of free tutorials, ranging from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced techniques. Channels like 3DBuzz, CG Cookie, and The Gnomon Workshop provide high-quality content from experienced artists and educators.
- 3ds Max Forums: Active online communities, such as the Autodesk forums, offer a platform to connect with fellow 3ds Max users, ask questions, share knowledge, and get feedback on your work.
Relevant Websites and Communities
Engaging with the 3ds Max community can provide invaluable insights, inspiration, and support.
- CGSociety: This renowned online community fosters a vibrant exchange of ideas and showcases the work of talented artists. You can find inspiration, participate in discussions, and connect with professionals in the field.
- Polycount: This forum focuses specifically on 3D modeling, offering a platform for discussions, critiques, and sharing of projects. You can find valuable feedback on your work and connect with like-minded individuals.
- ArtStation: This platform serves as a portfolio showcase for artists, providing inspiration and insights into the work of professionals. You can discover diverse styles, techniques, and trends in 3D modeling.
Books and Courses
For a structured and in-depth learning experience, consider exploring books and courses.
- “3ds Max for Beginners” by Michael J. C. Chambers: This book offers a comprehensive introduction to 3ds Max, covering fundamental concepts and techniques. It’s ideal for beginners looking for a solid foundation in the software.
- “3ds Max 2024: The Complete Guide” by Michael J. C. Chambers: This book provides a comprehensive guide to the latest version of 3ds Max, covering advanced features and workflows. It’s suitable for intermediate and advanced users.
- “The Gnomon Workshop: 3ds Max Tutorials”: The Gnomon Workshop offers a range of high-quality online courses taught by industry professionals. Their courses cover various aspects of 3ds Max, from modeling and animation to rendering and visual effects.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
3ds Max has become a cornerstone in various industries, impacting everything from visual storytelling to product design. Its versatility and powerful features have made it an indispensable tool for professionals across diverse sectors.
Architecture and Design
3ds Max is widely used in the architectural and design industries to create stunning visualizations, simulations, and renderings. It allows architects, designers, and engineers to bring their ideas to life in a realistic and immersive way.
- Architectural Visualization: Architects utilize 3ds Max to create photorealistic renderings of buildings, interiors, and landscapes. These renderings are used for presentations, marketing materials, and client approvals.
- Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences: 3ds Max plays a crucial role in developing immersive VR experiences for architectural walkthroughs and design explorations. Users can virtually explore buildings and spaces before they are built, allowing for informed decision-making.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): 3ds Max can be integrated with BIM software to create detailed 3D models that encompass all aspects of a building, from structural elements to finishes. This integration facilitates collaboration between different disciplines involved in the construction process.
Film and Animation
3ds Max is a go-to tool for creating high-quality visual effects, animations, and character modeling in the film and animation industry. It offers a comprehensive set of tools and features that empower artists to bring their creative visions to life.
- Character Animation: 3ds Max provides powerful tools for animating characters, including rigging, skinning, and motion capture integration. These features allow animators to create realistic and expressive character movements.
- Visual Effects (VFX): 3ds Max is widely used for creating realistic visual effects, such as explosions, smoke, and water simulations. Its particle systems and procedural modeling capabilities enable artists to achieve stunning visual results.
- 3D Modeling: 3ds Max allows artists to create intricate 3D models of characters, environments, and props. Its robust modeling tools enable them to sculpt, extrude, and manipulate geometry with precision.
Game Development
3ds Max is a valuable tool for game developers, enabling them to create high-quality assets, environments, and characters for their games. Its versatility and compatibility with game engines make it an essential part of the game development workflow.
- Level Design: 3ds Max is used to design and build game levels, creating intricate environments and interactive spaces for players to explore. Its modeling and texturing tools allow for detailed and visually engaging level creation.
- Character Modeling: 3ds Max is employed to create detailed 3D models of game characters, including their geometry, textures, and animations. Its rigging and skinning tools ensure smooth and realistic character movements.
- Asset Creation: Game developers use 3ds Max to create a wide range of game assets, such as weapons, vehicles, props, and environmental elements. Its modeling, texturing, and animation features facilitate the creation of high-quality assets.
Product Design and Manufacturing
3ds Max is increasingly used in product design and manufacturing to create prototypes, visualize products, and optimize designs. It enables designers and engineers to iterate on designs, explore different concepts, and create realistic representations of their products.
- Prototyping: 3ds Max allows designers to create 3D prototypes of products, enabling them to test form, function, and aesthetics before committing to physical production. This virtual prototyping process saves time and resources.
- Product Visualization: 3ds Max is used to create high-quality renderings and animations of products, showcasing their features and benefits to potential customers. These visualizations are used for marketing, sales, and design presentations.
- Design Optimization: 3ds Max can be used to analyze and optimize product designs, ensuring that they meet specific requirements and performance standards. Its modeling and simulation capabilities facilitate the identification and resolution of design flaws.
Marketing and Advertising
3ds Max is a powerful tool for creating engaging and visually compelling marketing and advertising materials. It enables designers to create realistic product mockups, 3D animations, and immersive experiences that capture attention and drive conversions.
- Product Mockups: 3ds Max allows designers to create realistic product mockups that can be used in marketing materials, websites, and social media campaigns. These mockups provide a compelling visual representation of products, enhancing their appeal.
- 3D Animations: 3ds Max is used to create eye-catching 3D animations for commercials, product demos, and social media content. These animations can effectively communicate product features, benefits, and brand messaging.
- Interactive Experiences: 3ds Max can be used to create interactive 3D experiences for marketing campaigns, allowing users to explore products, engage with brands, and learn about their offerings in a fun and immersive way.
Other Industries
3ds Max is also used in a wide range of other industries, including:
- Healthcare: 3ds Max is used for creating anatomical models, medical simulations, and surgical planning tools. It helps medical professionals visualize complex anatomical structures and develop innovative treatment strategies.
- Education: 3ds Max is used in educational settings to teach students about 3D modeling, animation, and design principles. It provides a hands-on learning experience that prepares students for careers in creative industries.
- Entertainment: 3ds Max is used for creating special effects, environments, and props for live events, concerts, and theatrical productions. It enhances the visual spectacle and immerses audiences in the experience.
Epilogue: 3d Studio Max
3D Studio Max stands as a testament to the power of technology in pushing the boundaries of creativity. Its comprehensive features and intuitive workflow make it an ideal tool for professionals and enthusiasts alike. As the world of 3D continues to evolve, 3ds Max remains at the forefront, empowering users to create stunning visuals that captivate audiences and inspire innovation. Whether you’re exploring the fundamentals of 3D modeling or delving into advanced techniques, 3ds Max provides the tools and resources to unlock your full creative potential.
3D Studio Max is a powerful software for creating stunning visuals, but sometimes you need to organize and analyze data to inform your designs. That’s where Microsoft Excel comes in. You can download Microsoft Excel for free and use its spreadsheet capabilities to manage budgets, track project progress, and even create charts to visualize your 3D model’s dimensions.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, integrating Excel into your workflow can enhance your 3D Studio Max experience.
